- SAP Community
- Groups
- Interest Groups
- Enterprise Architecture
- Blog Posts
- Understanding Business Capabilities and Business P...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Implementing an intelligent enterprise usually begins with a few core processes (e.g., customer management, distribution management, etc.), encompasses transactional processes (sales, procurement, accounts payable), and eventually includes unique and distinguishing business capabilities.
Building an intelligent enterprise doesn’t focus only on competitively distinctive capabilities—it also requires rationalizing and digitizing the mundane, everyday processes that a company has to get right to stay in business.
To build an intelligent enterprise, it’s essential to understand the relationship between Business capability and relevant Business Processes.
Business Capabilities:
A capability is defined as “an ability to do something.”
According to Ulrich Homann: “A business capability is a particular ability or capacity that a business may possess or exchange to achieve a specific purpose or outcome.”
It defines what a business does without explaining how, why, or where the company uses the capability.
Business capabilities are grouped using stratification (e.g. Strategic, Core, Support). Each stratification tier provides a different perspective or focal point.
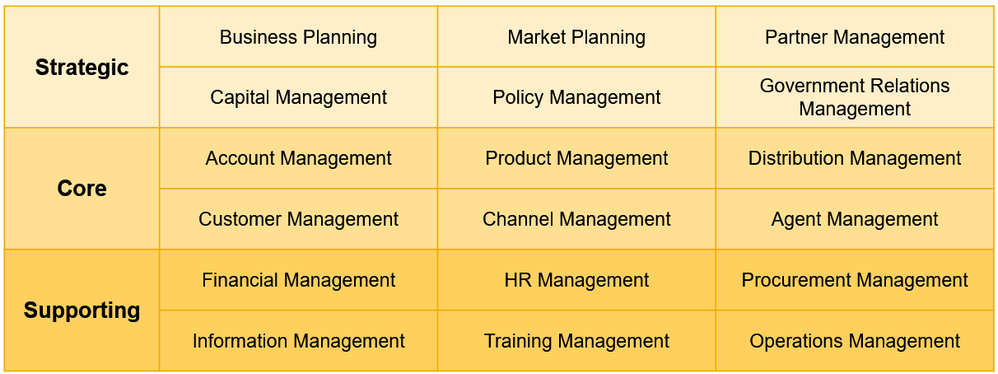
Business capabilities can also be grouped using leveling. Leveling is the process of decomposing each top-level (Level 1) business capability into lower levels (typically not more than three) to communicate more detail at a level appropriate for heat mapping and roadmap planning.
Business process:
A business process is a series of steps performed by stakeholders using information and technology to achieve business outcomes. Business Process defines “how do we do?”. How well these processes are standardized, integrated and executed will define the enterprises’ excellence in delivering the outcomes.
Processes are dynamic and continuously evolve based on changes in technology innovations and organizational changes.
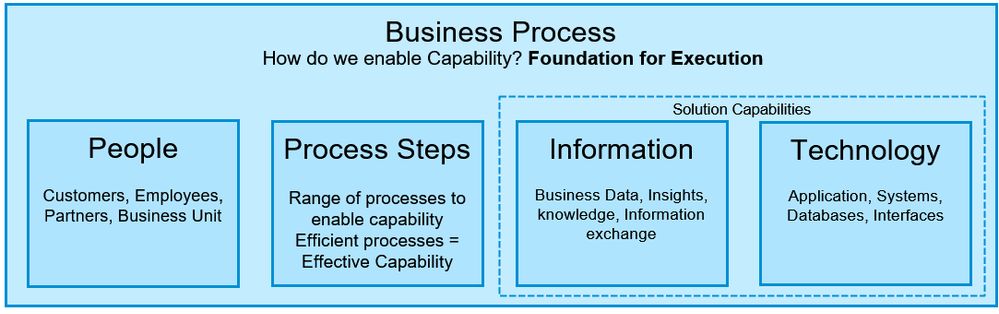
Figure 2 - Elements of Business Process
There are three components of a business process:
1. People
- People represent individuals, teams, business units, or partners involved in delivering a business capability
- People use technology and information and follow the process steps
2. Process steps / Activities
- Steps performed to deliver or enable realizing business capabilities.
- These steps can be performed by either People or the system
- Process steps can also be combined into modular processes or process segments
3. Solution Capabilities
- Solution capability is available technology and information to the people
3.1 Information
- The business data, knowledge, and insight
- Analytics and predictive scenarios based on algorithms
3.2 Technology
- Applications and Information technology systems
- Business Networks
- Process Automation
Notes on types of Business processes:
- Modular processes describe business steps within one business area, e.g. Perform Sourcing, Manage Purchasing, Manage Payables etc. Modular processes can able be broken down into Process segments and process steps
- End-to-end processes are a combination of various modular processes e.g. Source to Pay
- Managing mapping of process steps, process segments, modular processes and end-to-end processes can be a daunting task
Implementing an intelligent enterprise: An example
There are three pillars of implementing intelligent enterprise.
- Enhance solution capability by implementing Advanced applications, analytics and predictive algorithms, Process automation etc.
- Streamline and re-design processes to take advantage of new solution capabilities
- Enhance user experience by enabling new solution capabilities
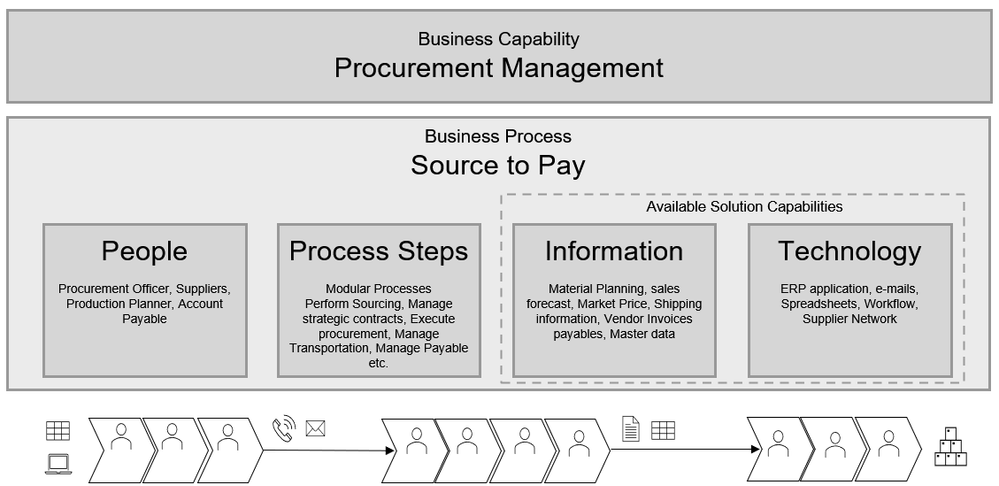
Traditional ERP – Business Process elements
The following represents a typical ‘Source to Pay” process in traditional ERP
- Many manual and disconnected processes that required continuous people intervention
- Dependent on the analysis performed by the people
- Limited use of newer technologies
Process maturity scale = 2 Legacy systems are used for transactions with limited automation. No automated integration with suppliers
Figure 3 -Business Process elements in traditional ERP
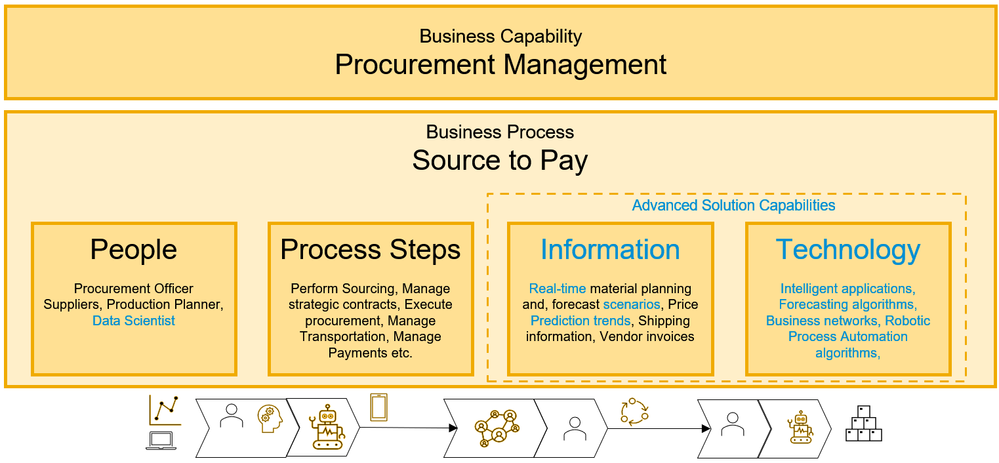
Intelligent ERP – Business Process elements
“Source to Pay” business process is enhanced by implementing business networks, process automation and advanced analytics tools. This will result in a better outcome for the business capability “Procurement management.”
- Automated and connected processes inside and across enterprise boundary
- Analytics and predictive algorithms enable people to improve decision
- Using technology to provide a better user experience and drive efficiency
Process maturity scale = 5 End-to-end integrations with suppliers. Leverage predictive analytics and process automation to improve decision-making and efficiency
Figure 4 - Business Process elements in intelligent ERP
Conclusion:
- Mapping business capability and business processes provide a common understanding of the business.
- This framework allows architects and decision-makers to focus their efforts on selecting the right solution capability to enhance a given business process that supports the organization’s strategic objective.
- An intelligent enterprise integrates today’s intelligent technologies in digitizing business processes to improve a company’s core capabilities.
Reference:
- TOGAF Business Capabilities Guide V2 (opengroup.org)
- Enterprise Architecture as a strategy 2006; Authors: Jeanne W. Ross, Peter Weill, and David C. Rober...
- SAP Intelligent Enterprise – Whitepaper
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
Application Architecture
23 -
Business Architecture
33 -
Data Architecture
19 -
Emerging Trends
20 -
Enterprise Architecture
53 -
Frameworks
20 -
Hybrid and Multi Cloud
3 -
Innovation
14 -
Integration Architecture
16 -
Portuguese
1 -
Roadmaps
12 -
Skills and Learning
29 -
Solution Architecture
22 -
Sustainability
3 -
Technology Architecture
23 -
Tools
14
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 7 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 1 | |
| 1 | |
| 1 | |
| 1 | |
| 1 | |
| 1 |