
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Technology
- Technology Blogs by Members
- Part 2 – SAP MDG – A Stepping Stone for SAP S/4HAN...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Introduction
Clients across the globe are getting into the transformation journey started with SAP S/4HANA.
In this blog, we will take one of the use cases to discuss how the master data (MDG) journey will be the stepping stone for SAP S/4HANA Transformation and the needed steps to achieve it.
This is the second blog on this topic. For Part 1, kindly refer
https://blogs.sap.com/2023/01/27/sap-mdg-a-stepping-stone-for-sap-s-4hana-journey-part-i/
Use Case ( Recap)
Business Context
- In the current landscape, there are 3 separate SAP ECC instances for each region: APAC, Europe and the Americas
- The business process for both master data and transactional data is different by country within a single Region ( ECC instance) and also across regions ( Other ECC Instances)
- The best practices are not fully adhered to in many cases, so in the long run, it is expected to optimise the process for better efficiency
IT Context
- In the roadmap, a single instance of SAP S/4HANA to replace the 3 separate ECC instances in the phased manner
- A dedicated master data system to ensure the governance, data quality and unified master data send across the landscape for business operations
Key Aspects for MDG : Deep Dive
A. Initial Setup
A.2 Account Group Consolidation ( As needed)
As MDG going to the central master data systems catering for 3 ECC systems & future S/4 system, it is important to finalize the account groups
Customer master will be taken as an example for this discussion
Current State in ECC
In the current ECC system, due to the existing business process, there could be multiple account groups for the same definition

In the above example, we have 2 types of challenging scenarios
- In Europe, the Sold-To account have been created by business units to bifurcate the customers
- In Americas, Sold-To account have been created by regions
The field properties, number ranges could be different for these account groups. The account group have been setup to have duplicate within the ECC due to the existing way of working.
What’s for MDG
For setting up account groups in MDG, we have 6 different account groups that have duplicates within & across ECCs.
For MDG, what should be the design of account groups; Can we do a Lift and shift of existing account groups into MDG?
The answer is “Definitely No”. We need to see the opportunity to unify and harmonise account groups.
High-Level Overview
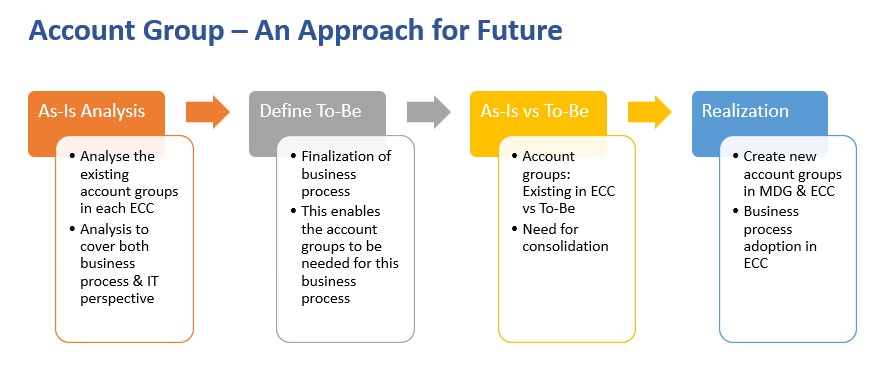
- Account Groups: As-Is Analysis
The account group analysis needs to be done in various dimensions

This analysis provides the insights and usages of account groups across business processes, IT dependency will enable to take the right decision for future design
2. Define To-Be
As MDG is considered as the stepping stone for future SAP S/4HANA program, the account group setting needs to be aligned with the future.
The account groups can't be created independently without understanding or finalization of future business processes.
The keywords are business process standardization & business process optimization.

The functional experts from each stream such as SOTC, P2P,R2R will be conducting the Fit-To-Standard workshops to get the requirements/needs of any customization
In the given example, there are multiple Sold-To’s in an ECC. The As-Is analysis will give an insight into whether it is done for Legal / Fiscal / Statutory needs. If No, we have an opportunity here
A decision needs to be made whether the same process is to be taken in to future state as well. If that’s not the case, it needs to be taken under either standardization/optimization
The finalization of the business process & solution design will provide the finalized account group to be taken forward
3. As-Is vs To-Be
New Account Group Definition: Field Properties and Number ranges need to be done
The existing account groups need to be compared against the newly finalised account groups

Account Groups Consolidation
Account Group Standardization: In the given example, based on the Fit-To-Standard, there is a decision to stick to 1 account group for Sold-To.
This brings the account group consolidation on the ECC side from the business process perspective
Data Perspective
- Legacy Data (Existing) – There will not be changes to the account group for the existing master data. However there would be data quality-specific activities such as enrichment, and deduplication needs to be done to enable data migration & quality. This will be discussed in detail in the data migration section (C.3)
- New Master Data (Post MDG) – New master data will be created in the new account group and sent it to ECC. In ECC, it will be created under a new account group
While the account group is discussed here, the Business Partner (BP) Group strategy needs to be defined as well. This will be discussed in S/4HANA specific section (C.2)
4. Realization
The new account groups need to be configured in MDG and also in each ECC system.
Remediation
Based on the As-Is analysis, the identified impact on transactions, interface, data needs to be remediated in ECCs to run the business process for new account groups
As there is a mix of master data with old account groups and new account groups in ECC systems, the remediation needs to be done in such a as way to support both.
Reporting and downstream systems are a few of the key factors to be considered with the mixed-operating master data model
In Section E, there will be a brief on the approach of tools, risk, and testing on the remediation
Business Process Adoption
By this enablement, the business process needs to follow the standardized model. Which means there is a change / adoption needs to do so in ECC.
The system-related (technology) will be covered by remediation; people & processes related to be handled through a change management process such as training , documentation etc.
A.3 Number Ranges
Once the account group have been finalised, the key topic would be the number ranges.
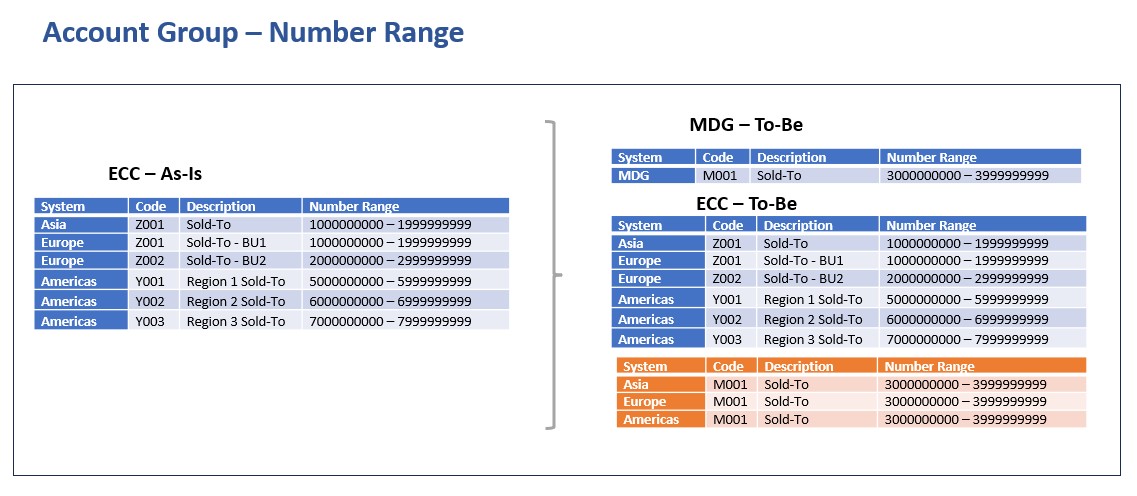
Following are some of the key factors to be considered for number range finalization
- The number range to be checked across all ECC systems and find out the available slot
- As-Is Analysis: Whether any intelligent numbering has been used
- To-Be: The opportunity to move into a non-intelligent numbering
- Internal or External Numbering
- Same number range to be used for various account groups for a master data object (Ex. Customer) vs Specific number range by account group within a master data object
Various topics discussed in the account group section will apply to Number ranges as well.
General Questions
In the transformation program, generally, there will be questions as below related to the account group & number range which can be covered in this section :
Why I should Go Away from Intelligent Numbering as it does work perfectly today?
Intelligent numbering of the master data is a common practice across organizations in the legacy world.
People, Processes and Technology have been made to support intelligent numbering to make the process work.
Is this a concern for standardization, and data quality? A point of view on this topic

What are the benefits of business process standardization & consolidation of account groups done in ECC ahead of SAP S/4HANA, knowing the fact that ECC will go away with SAP S/4HANA in the future?
Preparation Work
- For any transformation program, business case creation is the first step.
- Identifying the key pain points and areas of improvements
- Creating measurable KPIs for business value realization
- Have alignment on Return on Investment (ROI) with a timeline plan
With the above preparation work done for the MDG program, the following could be additional dimensions to be considered for response
- What is the timeline of MDG solution connected to each of ECC’s systems?
- What is the timeline of interim period , some of ECC’s system still operative, while the other is already implemented on SAP S/4HANA?
- What will the overall timeline from MDG program start to End state – 1 SAP S/4HANA?
The timeline & current pain points will provide the initial idea in terms of investing in ECC’s for remediation.
- Before starting the SAP S/4HANA, having multiple preparation projects will help to solve issues ahead
- Another key is having a clear end state, strategy and vision will help the investment on ECC’s being beneficial for S/4HANA program.
In the next blog, I will cover other topics in detail.
About the Author,
Antony Prasanna has been working in SAP master data space since 2006. Have experience working across multiple large transformation programs on SAP S/4HANA including SAP MDM, MDG and Data Migration tools.
- SAP Managed Tags:
- SAP Master Data Governance
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
"automatische backups"
1 -
"regelmäßige sicherung"
1 -
"TypeScript" "Development" "FeedBack"
1 -
505 Technology Updates 53
1 -
ABAP
18 -
ABAP API
1 -
ABAP CDS Views
4 -
ABAP CDS Views - BW Extraction
1 -
ABAP CDS Views - CDC (Change Data Capture)
1 -
ABAP class
2 -
ABAP Cloud
3 -
ABAP DDIC CDS view
1 -
ABAP Development
5 -
ABAP in Eclipse
3 -
ABAP Platform Trial
1 -
ABAP Programming
2 -
abap technical
1 -
abapGit
1 -
absl
2 -
access data from SAP Datasphere directly from Snowflake
1 -
Access data from SAP datasphere to Qliksense
1 -
Accrual
1 -
action
1 -
adapter modules
1 -
Addon
1 -
Adobe Document Services
1 -
ADS
1 -
ADS Config
1 -
ADS with ABAP
1 -
ADS with Java
1 -
ADT
2 -
Advance Shipping and Receiving
1 -
Advanced Event Mesh
3 -
Advanced formula
1 -
AEM
1 -
AI
8 -
AI Launchpad
1 -
AI Projects
1 -
AIML
10 -
Alert in Sap analytical cloud
1 -
Amazon S3
1 -
Analytic Models
1 -
Analytical Dataset
1 -
Analytical Model
1 -
Analytics
1 -
Analyze Workload Data
1 -
annotations
1 -
API
1 -
API and Integration
4 -
API Call
2 -
API security
1 -
Application Architecture
1 -
Application Development
5 -
Application Development for SAP HANA Cloud
3 -
Applications and Business Processes (AP)
1 -
Artificial Intelligence
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
5 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) 1 Business Trends 363 Business Trends 8 Digital Transformation with Cloud ERP (DT) 1 Event Information 462 Event Information 15 Expert Insights 114 Expert Insights 76 Life at SAP 418 Life at SAP 1 Product Updates 4
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise Oil Gas IoT Exploration Production
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise sustainability responsibility esg social compliance cybersecurity risk
1 -
AS Java
1 -
ASE
1 -
ASR
2 -
Asset Management
2 -
Associations in CDS Views
1 -
ASUG
1 -
Attachments
1 -
Authentication
1 -
Authorisations
1 -
Automating Processes
1 -
Automation
2 -
aws
2 -
Azure
2 -
Azure AI Studio
1 -
Azure API Center
1 -
Azure API Management
1 -
B2B Integration
1 -
Background job
1 -
Backorder Processing
1 -
Backpropagation
1 -
Backup
1 -
Backup and Recovery
1 -
Backup schedule
1 -
BADI_MATERIAL_CHECK error message
1 -
Bank
1 -
Bank Communication Management
1 -
BAS
1 -
basis
2 -
Basis Monitoring & Tcodes with Key notes
2 -
Batch Management
1 -
BDC
1 -
Best Practice
1 -
BI
1 -
bitcoin
1 -
Blockchain
3 -
bodl
1 -
BOP in aATP
1 -
BOP Segments
1 -
BOP Strategies
1 -
BOP Variant
1 -
BPC
1 -
BPC LIVE
1 -
BTP
14 -
BTP AI Launchpad
1 -
BTP Destination
2 -
Business AI
1 -
Business and IT Integration
1 -
Business application stu
1 -
Business Application Studio
1 -
Business Architecture
1 -
Business Communication Services
1 -
Business Continuity
2 -
Business Data Fabric
3 -
Business Fabric
1 -
Business Partner
13 -
Business Partner Master Data
11 -
Business Technology Platform
2 -
Business Trends
4 -
BW4HANA
1 -
CA
1 -
calculation view
1 -
CAP
4 -
Capgemini
1 -
CAPM
1 -
Catalyst for Efficiency: Revolutionizing SAP Integration Suite with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and
1 -
CCMS
2 -
CDQ
13 -
CDS
2 -
CDS Views
1 -
Cental Finance
1 -
Certificates
1 -
CFL
1 -
Change Management
1 -
chatbot
1 -
chatgpt
3 -
CICD
1 -
CL_SALV_TABLE
2 -
Class Runner
1 -
Classrunner
1 -
Cloud ALM Monitoring
1 -
Cloud ALM Operations
1 -
cloud connector
1 -
Cloud Extensibility
1 -
Cloud Foundry
4 -
Cloud Integration
6 -
Cloud Platform Integration
2 -
cloudalm
1 -
communication
1 -
Compensation Information Management
1 -
Compensation Management
1 -
Compliance
1 -
Compound Employee API
1 -
Configuration
1 -
Connectors
1 -
Consolidation
1 -
Consolidation Extension for SAP Analytics Cloud
3 -
Control Indicators.
1 -
Controller-Service-Repository pattern
1 -
Conversion
1 -
Corrective Maintenance
1 -
Cosine similarity
1 -
CPI
1 -
cryptocurrency
1 -
CSI
1 -
ctms
1 -
Custom chatbot
3 -
Custom Destination Service
1 -
custom fields
1 -
Custom Headers
1 -
Customer Experience
1 -
Customer Journey
1 -
Customizing
1 -
cyber security
4 -
cybersecurity
1 -
Data
1 -
Data & Analytics
1 -
Data Aging
1 -
Data Analytics
2 -
Data and Analytics (DA)
1 -
Data Archiving
1 -
Data Back-up
1 -
Data Flow
1 -
Data Governance
5 -
Data Integration
2 -
Data Quality
13 -
Data Quality Management
13 -
Data Synchronization
1 -
data transfer
1 -
Data Unleashed
1 -
Data Value
9 -
Database and Data Management
1 -
database tables
1 -
Databricks
1 -
Dataframe
1 -
Datasphere
3 -
datenbanksicherung
1 -
dba cockpit
1 -
dbacockpit
1 -
Debugging
2 -
Defender
1 -
Delimiting Pay Components
1 -
Delta Integrations
1 -
Destination
3 -
Destination Service
1 -
Developer extensibility
1 -
Developing with SAP Integration Suite
1 -
Devops
1 -
digital transformation
1 -
Disaster Recovery
1 -
Documentation
1 -
Dot Product
1 -
DQM
1 -
dump database
1 -
dump transaction
1 -
e-Invoice
1 -
E4H Conversion
1 -
Eclipse ADT ABAP Development Tools
2 -
edoc
1 -
edocument
1 -
ELA
1 -
Embedded Consolidation
1 -
Embedding
1 -
Embeddings
1 -
Emergency Maintenance
1 -
Employee Central
1 -
Employee Central Payroll
1 -
Employee Central Time Off
1 -
Employee Information
1 -
Employee Rehires
1 -
Enable Now
1 -
Enable now manager
1 -
endpoint
1 -
Enhancement Request
1 -
Enterprise Architecture
1 -
Enterprise Asset Management
2 -
Entra
1 -
ESLint
1 -
ETL Business Analytics with SAP Signavio
1 -
Euclidean distance
1 -
Event Dates
1 -
Event Driven Architecture
1 -
Event Mesh
2 -
Event Reason
1 -
EventBasedIntegration
1 -
EWM
1 -
EWM Outbound configuration
1 -
EWM-TM-Integration
1 -
Existing Event Changes
1 -
Expand
1 -
Expert
2 -
Expert Insights
2 -
Exploits
1 -
Fiori
16 -
Fiori App Extension
2 -
Fiori Elements
2 -
Fiori Launchpad
2 -
Fiori SAPUI5
13 -
first-guidance
1 -
Flask
2 -
FTC
1 -
Full Stack
9 -
Funds Management
1 -
gCTS
1 -
GenAI hub
1 -
General
2 -
Generative AI
1 -
Getting Started
1 -
GitHub
11 -
Google cloud
1 -
Grants Management
1 -
groovy
2 -
GTP
1 -
HANA
6 -
HANA Cloud
2 -
Hana Cloud Database Integration
2 -
HANA DB
2 -
Hana Vector Engine
1 -
HANA XS Advanced
1 -
Historical Events
1 -
home labs
1 -
HowTo
1 -
HR Data Management
1 -
html5
9 -
HTML5 Application
1 -
Identity cards validation
1 -
idm
1 -
Implementation
1 -
Improvement Maintenance
1 -
Infuse AI
1 -
input parameter
1 -
instant payments
1 -
Integration
3 -
Integration Advisor
1 -
Integration Architecture
1 -
Integration Center
1 -
Integration Suite
1 -
intelligent enterprise
1 -
Internal Table
1 -
iot
1 -
Java
1 -
JMS Receiver channel ping issue
1 -
job
1 -
Job Information Changes
1 -
Job-Related Events
1 -
Job_Event_Information
1 -
joule
4 -
Journal Entries
1 -
Just Ask
1 -
Kerberos for ABAP
10 -
Kerberos for JAVA
9 -
KNN
1 -
Launch Wizard
1 -
Learning Content
2 -
Life at SAP
5 -
lightning
1 -
Linear Regression SAP HANA Cloud
1 -
Loading Indicator
1 -
local tax regulations
1 -
LP
1 -
Machine Learning
4 -
Marketing
1 -
Master Data
3 -
Master Data Management
15 -
Maxdb
2 -
MDG
1 -
MDGM
1 -
MDM
1 -
Message box.
1 -
Messages on RF Device
1 -
Microservices Architecture
1 -
Microsoft
1 -
Microsoft Universal Print
1 -
Middleware Solutions
1 -
Migration
5 -
ML Model Development
1 -
MLFlow
1 -
Modeling in SAP HANA Cloud
9 -
Monitoring
3 -
MPL
1 -
MTA
1 -
Multi-factor-authentication
1 -
Multi-Record Scenarios
1 -
Multilayer Perceptron
1 -
Multiple Event Triggers
1 -
Myself Transformation
1 -
Neo
1 -
Neural Networks
1 -
New Event Creation
1 -
New Feature
1 -
Newcomer
1 -
NodeJS
3 -
ODATA
2 -
OData APIs
1 -
odatav2
1 -
ODATAV4
1 -
ODBC
1 -
ODBC Connection
1 -
Onpremise
1 -
open source
2 -
OpenAI API
1 -
Oracle
1 -
Overhead and Operational Maintenance
1 -
PaPM
1 -
PaPM Dynamic Data Copy through Writer function
1 -
PaPM Remote Call
1 -
Partner Built Foundation Model
1 -
PAS-C01
1 -
Pay Component Management
1 -
PGP
1 -
Pickle
1 -
PLANNING ARCHITECTURE
1 -
Plant Maintenance
2 -
Popup in Sap analytical cloud
1 -
PostgrSQL
1 -
POSTMAN
1 -
Prettier
1 -
Proactive Maintenance
1 -
Process Automation
2 -
Product Updates
6 -
PSM
1 -
Public Cloud
1 -
Python
5 -
python library - Document information extraction service
1 -
Qlik
1 -
Qualtrics
1 -
RAP
3 -
RAP BO
2 -
React
1 -
Reactive Maintenance
2 -
Record Deletion
1 -
Recovery
1 -
recurring payments
1 -
redeply
1 -
Release
1 -
Remote Consumption Model
1 -
Replication Flows
1 -
Report Malfunction
1 -
report painter
1 -
research
1 -
Resilience
1 -
REST
1 -
REST API
1 -
Retagging Required
1 -
Risk
1 -
rolandkramer
2 -
Rolling Kernel Switch
1 -
route
1 -
rules
1 -
S4 HANA
1 -
S4 HANA Cloud
1 -
S4 HANA On-Premise
1 -
S4HANA
6 -
S4HANA Cloud
1 -
S4HANA_OP_2023
2 -
SAC
11 -
SAC PLANNING
10 -
SAP
4 -
SAP ABAP
1 -
SAP Advanced Event Mesh
1 -
SAP AI Core
10 -
SAP AI Launchpad
9 -
SAP Analytic Cloud
1 -
SAP Analytic Cloud Compass
1 -
Sap Analytical Cloud
1 -
SAP Analytics Cloud
5 -
SAP Analytics Cloud for Consolidation
3 -
SAP Analytics cloud planning
1 -
SAP Analytics Cloud Story
1 -
SAP analytics clouds
1 -
SAP API Management
1 -
SAP Application Logging Service
1 -
SAP BAS
1 -
SAP Basis
6 -
SAP BO FC migration
1 -
SAP BODS
1 -
SAP BODS certification.
1 -
SAP BODS migration
1 -
SAP BPC migration
1 -
SAP BTP
25 -
SAP BTP Build Work Zone
2 -
SAP BTP Cloud Foundry
8 -
SAP BTP Costing
1 -
SAP BTP CTMS
1 -
SAP BTP Generative AI
1 -
SAP BTP Innovation
1 -
SAP BTP Migration Tool
1 -
SAP BTP SDK IOS
1 -
SAP BTPEA
1 -
SAP Build
12 -
SAP Build App
1 -
SAP Build apps
1 -
SAP Build CodeJam
1 -
SAP Build Process Automation
3 -
SAP Build work zone
11 -
SAP Business Objects Platform
1 -
SAP Business Technology
2 -
SAP Business Technology Platform (XP)
1 -
sap bw
1 -
SAP CAP
2 -
SAP CDC
1 -
SAP CDP
1 -
SAP CDS VIEW
1 -
SAP Certification
1 -
SAP Cloud ALM
4 -
SAP Cloud Application Programming Model
1 -
SAP Cloud Integration
1 -
SAP Cloud Integration for Data Services
1 -
SAP cloud platform
9 -
SAP Companion
1 -
SAP CPI
3 -
SAP CPI (Cloud Platform Integration)
2 -
SAP CPI Discover tab
1 -
sap credential store
1 -
SAP Customer Data Cloud
1 -
SAP Customer Data Platform
1 -
SAP Data Intelligence
1 -
SAP Data Migration in Retail Industry
1 -
SAP Data Services
1 -
SAP DATABASE
1 -
SAP Dataspher to Non SAP BI tools
1 -
SAP Datasphere
9 -
SAP DRC
1 -
SAP EWM
1 -
SAP Fiori
3 -
SAP Fiori App Embedding
1 -
Sap Fiori Extension Project Using BAS
1 -
SAP GRC
1 -
SAP HANA
1 -
SAP HANA PAL
1 -
SAP HANA Vector
1 -
SAP HCM (Human Capital Management)
1 -
SAP HR Solutions
1 -
SAP IDM
1 -
SAP Integration Suite
10 -
SAP Integrations
4 -
SAP iRPA
2 -
SAP LAGGING AND SLOW
1 -
SAP Learning Class
1 -
SAP Learning Hub
1 -
SAP Master Data
1 -
SAP Odata
3 -
SAP on Azure
2 -
SAP PAL
1 -
SAP PartnerEdge
1 -
sap partners
1 -
SAP Password Reset
1 -
SAP PO Migration
1 -
SAP Prepackaged Content
1 -
sap print
1 -
SAP Process Automation
2 -
SAP Process Integration
2 -
SAP Process Orchestration
1 -
SAP Router
1 -
SAP S4HANA
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud
3 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud for Finance
1 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud private edition
1 -
SAP Sandbox
1 -
SAP STMS
1 -
SAP successfactors
3 -
SAP SuccessFactors HXM Core
1 -
SAP Time
1 -
SAP TM
2 -
SAP Trading Partner Management
1 -
SAP UI5
1 -
SAP Upgrade
1 -
SAP Utilities
1 -
SAP-GUI
9 -
SAP_COM_0276
1 -
SAPBTP
1 -
SAPCPI
1 -
SAPEWM
1 -
sapfirstguidance
3 -
SAPHANAService
1 -
SAPIQ
2 -
sapmentors
1 -
saponaws
2 -
saprouter
1 -
SAPRouter installation
1 -
SAPS4HANA
1 -
SAPUI5
5 -
schedule
1 -
Script Operator
1 -
Secure Login Client Setup
9 -
security
10 -
Selenium Testing
1 -
Self Transformation
1 -
Self-Transformation
1 -
SEN
1 -
SEN Manager
1 -
Sender
1 -
service
2 -
SET_CELL_TYPE
1 -
SET_CELL_TYPE_COLUMN
1 -
SFTP scenario
2 -
Simplex
1 -
Single Sign On
9 -
Singlesource
1 -
SKLearn
1 -
Slow loading
1 -
SOAP
2 -
Software Development
1 -
SOLMAN
1 -
solman 7.2
2 -
Solution Manager
3 -
sp_dumpdb
1 -
sp_dumptrans
1 -
SQL
1 -
sql script
1 -
SSL
9 -
SSO
9 -
Story2
1 -
Substring function
1 -
SuccessFactors
1 -
SuccessFactors Platform
1 -
SuccessFactors Time Tracking
1 -
Sybase
1 -
Synthetic User Monitoring
1 -
system copy method
1 -
System owner
1 -
Table splitting
1 -
Tax Integration
1 -
Technical article
1 -
Technical articles
1 -
Technology Updates
15 -
Technology Updates
1 -
Technology_Updates
1 -
terraform
1 -
Testing
1 -
Threats
2 -
Time Collectors
1 -
Time Off
2 -
Time Sheet
1 -
Time Sheet SAP SuccessFactors Time Tracking
1 -
Tips and tricks
2 -
toggle button
1 -
Tools
1 -
Trainings & Certifications
1 -
Transformation Flow
1 -
Transport in SAP BODS
1 -
Transport Management
1 -
TypeScript
3 -
ui designer
1 -
unbind
1 -
Unified Customer Profile
1 -
UPB
1 -
Use of Parameters for Data Copy in PaPM
1 -
User Unlock
1 -
VA02
1 -
Validations
1 -
Vector Database
2 -
Vector Engine
1 -
Vectorization
1 -
Visual Studio Code
1 -
VSCode
2 -
VSCode extenions
1 -
Vulnerabilities
1 -
Web SDK
1 -
Webhook
1 -
work zone
1 -
workload
1 -
xsa
1 -
XSA Refresh
1
- « Previous
- Next »
- Be a Cockroach: A Simple Guide to AI and SAP Full-Stack Development - Part I in Technology Blogs by Members
- Part 4 - SAP MDG – A Stepping Stone for SAP S/4HANA Journey in Technology Blogs by Members
- Part 3 – SAP MDG – A Stepping Stone for SAP S/4HANA Journey in Technology Blogs by Members
- OUT NOW: SAP Signavio February 2024 release in Technology Blogs by SAP
- How to configure and setup SAP Build Process Automation Part 1/2 in Technology Blogs by SAP
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 53 | |
| 5 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 |