- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Product Lifecycle Management
- PLM Blogs by SAP
- Striking the Perfect Balance
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Traditionally, product development has revolved around three key challenges: Velocity, Quality and Profitability. However, a fourth dimension, Sustainability, has now emerged as a critical aspect. The interconnectedness of these factors necessitates the need to have immediate availability of product-related information from across the enterprise to make intelligent real-time trade-off decisions. True innovation can only be achieved when product lifecycle management (PLM) is tightly connected to the enterprise resource planning (ERP) environment. By leveraging the integrated capabilities of PLM and ERP, organizations can enhance their ability to meet market demands, improve product quality, optimize profitability and address sustainability concerns.
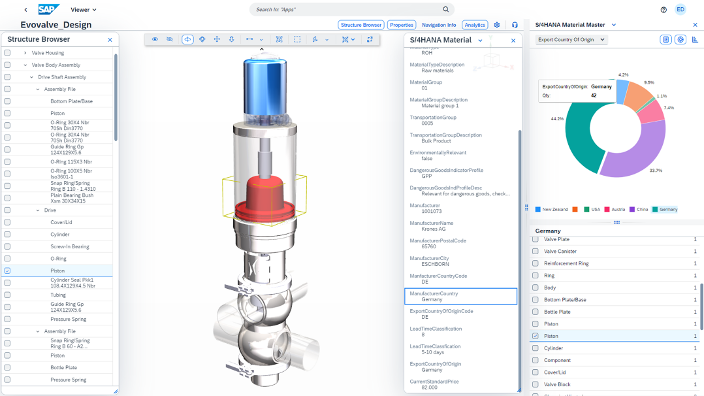
Image 1: Infusing product design information with real-time business data enables everyone to make more informed decisions in the context of the design.
SAP is acutely aware of these dynamics and aims to deliver the tools product development organizations need to bring their products to market. The value of PLM is enhanced when integrated to business data in ERP, especially when the integration is delivered natively. By leveraging data-driven insights throughout the sustainable product innovation process, SAP endeavors to enable a seamless product definition across the enterprise for all stakeholders involved in delivering products that meet evolving customer expectations.
Let’s walk through a typical end-to-end process where we define the needs for new products, collaboratively develop these products and deliver the product definition for downstream consumption, all while managing data across the extended enterprise.
Defining New Products
Innovation is the lifeblood of an organization. It is crucial to continuously foster innovation through a process that encourages the submission of new ideas and inputs from various stakeholders. These ideas could come directly from customers, employees, suppliers, social media, analyst reviews, market research, operational performance data, IoT, etc. Providing an open and collaborative process for the collection of these ideas and insights allows the innovation process to easily be enriched and diversified.
Ideas need to be prioritized based upon strategic value to the organization as well as upon criteria like risk, budget and resource availability. You need to ensure you can bring the right products to market at the right time and be able to make continuous portfolio decisions on what the right mix of ideas is to execute upon.
Defining the detailed product requirements for these new innovations is also important in this phase. You need to track not only what product features are needed to meet the customer needs but also what requirements must be met to comply with corporate goals like brand value and sustainability.
The process of defining new products or formulations should be target-driven and data supported. Setting targets and requirements helps set the guardrails to guide decisions when tradeoffs need to occur. For example, whether changing material A for material B affects cost, recyclability, product reliability, etc. By setting clear requirements for product development, companies can ensure that innovation efforts are directed towards achieving desired outcomes.
Developing a Product
In the context of developing new products or formulations, companies are increasingly relying on 3D CAD tools to model the product or formulation tools to develop the recipe and process steps. When these tools are integrated into the ERP layer, a more efficient and accurate product development process is achievable because data is not being duplicated and maintained across disparate systems.
Companies now need to support “hybrid” scenarios, where different disciplines such as mechanical, electrical and software engineering come together. In discrete industries like industrial machinery, these hybrid scenarios involve integrating mechanical, electrical and software components. In process industries, such as life sciences, these hybrid scenarios involve developing both the formulated product and the discrete device used to deliver the product to the patient.
Companies not only require tools to develop new products and formulations but also tools to modify existing products. However, any changes made must be done in the context of an ERP system to understand the true impact of the change (i.e., the impact on planned production, current inventory, cost, etc.). SAP natively provides this view through a tight connection between PLM and ERP.
Delivering a Product Definition
Transitioning product information out of product development to the enterprise is an important process that should be seamless. This transition includes not only the final release of the product but is also needed during the design process to support activities like sourcing and procurement for long lead items, as well as providing detailed product information for contract manufacturing. Product design information is relevant to all operations downstream (i.e., manufacturing, service, sales, etc.).
When you can have native integration of product data throughout its lifecycle (a true Digital Thread), from design through retirement you have a web of information that connects every operational detail directly in context of the product design. The digital thread provides feedback loop back into product development and into the define phase, allowing for a continuous improvement process.
Overall, the goal is to ensure that product information flows smoothly from product development to the rest of the enterprise, enabling effective collaboration and enhancing the overall product lifecycle.
Managing Products Across an Enterprise
In the product development process, it is important to recognize that design processes cannot operate in isolation from one another. Various factors such as profitability, compliance and sustainability need to be continuously assessed throughout the process.
Compliance and sustainability play vital roles in product development by guiding ethical ideation, ensuring safety and validating regulatory adherence. Designers and formulators require solutions to understand these topics and how their design choices affect adherence to these factors as well as how their decisions affect profitability. Tight integration of the PLM data with ERP provides the ability to not only measure and monitor effectively, but also to make informed decisions across the entire development process. It is crucial for you to have easy access to the complete set of product-related information across the enterprise to drive effective product innovation.
SAP is committed to providing the solutions necessary to drive true innovation in product development. By leveraging a natively integrated PLM+ERP environment, like the one offered by SAP, engineers and formulators can efficiently define, develop and deliver sustainable and profitable products that meet customer needs.
To learn more about how SAP can support your product development process, we invite you to explore our future articles in this series and visit our website.
- SAP Managed Tags:
- PLM (Product Lifecycle Management)
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
- A Comprehensive Breakdown: The Pros and Cons of Product Lifecycle Management in Product Lifecycle Management Blogs by SAP
- Navigating the Cloud Conundrum: Insights on Hybrid PLM | ft. panel of experts in Product Lifecycle Management Blogs by SAP
- StartupWeekend Stuttgart 2013 off to a great start in Product Lifecycle Management Blogs by SAP