- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Supply Chain Management
- SCM Blogs by SAP
- Nonconformance Codes in SAP Digital Manufacturing
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Introduction
Quality is super important in manufacturing. But sometimes, even with strict rules and checks, things don't go as planned. It's really important to handle these situations well to keep products good and customers happy. That's where Nonconformances in SAP Digital Manufacturing come in handy.
In this blog post, we will explore the basics about Nonconformance capabilities within SAP Digital Manufacturing.
Nonconformance Capability
SAP Digital Manufacturing nonconformance capability provides a mechanism for logging, tracking and dispositioning of failed or defective parts, enabling the following outcomes:
- Document the nonconformance management process using a closed loop system.
- Exclude nonconforming parts / materials from the production process.
- Trigger nonconformance work tasks for the assigned resources and provide traceability.
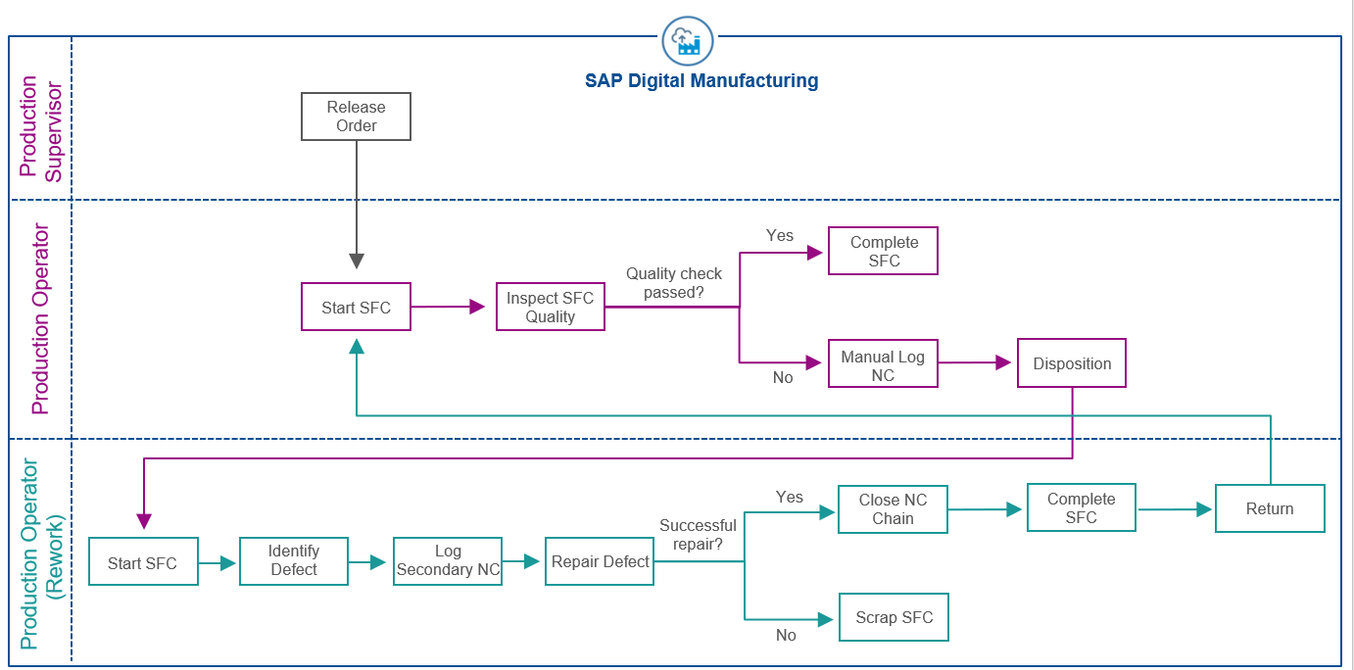
In general, nonconformance flow can fit in the overall manufacturing process as shown in the diagram below:
What are Nonconformance Codes?
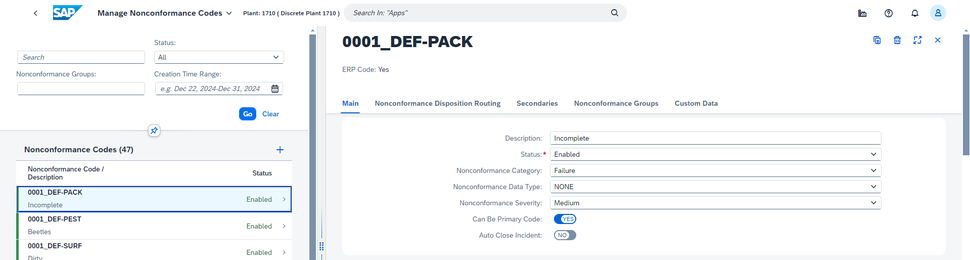
Nonconformance codes represent a deviation from standards, a defect, or an issue in production and provide a structured way to document these occurrences.
See below how NC codes are defined:
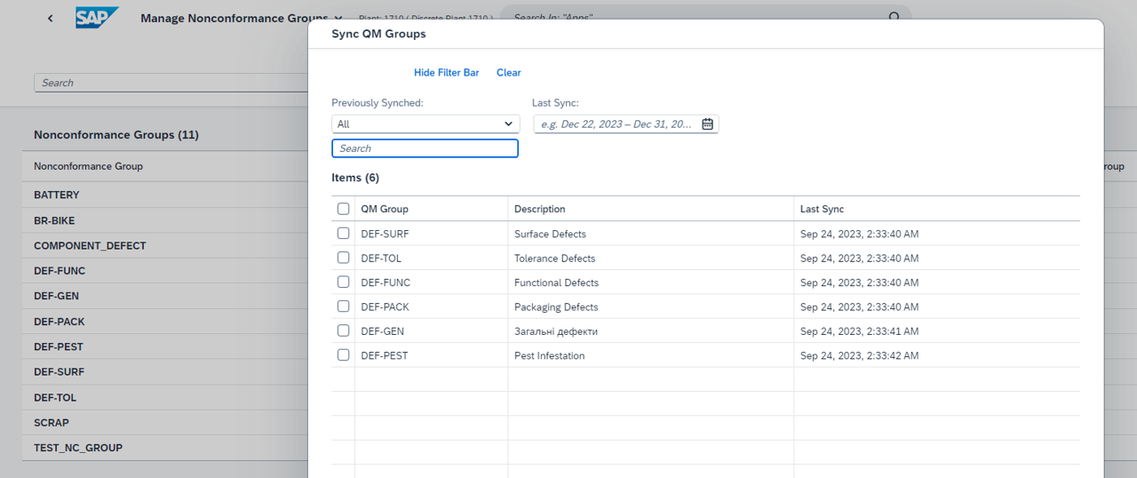
Nonconformance Codes can also be transfered directly from ERP Quality Management (QM) module via Nonconformance Groups, see Transferring QM Defect Code Groups and Codes from S/4HANA Cloud or S/4HANA On Prem for more details, as follows:
* When you log a nonconformance using a defect code originated from ERP Quality Management (QM) module, it is automatically transferred back to SAP ERP and a generic defect record is created.
Or manually created directly in SAP Digital Manufacturing via Manage Nonconformance Groups and Manage Nonconformance Codes apps.
Categorization and Hierarchy
NC codes can be categorized as primary or secondary, forming hierarchies that reflect the complexity of nonconformances. Primary codes represent the main issue, while secondary codes can go deeper into specific aspects like root causes or corrective actions. This hierarchical structure allows for granular tracking and analysis of nonconformance data. See below how a NC code hierarchy is defined:
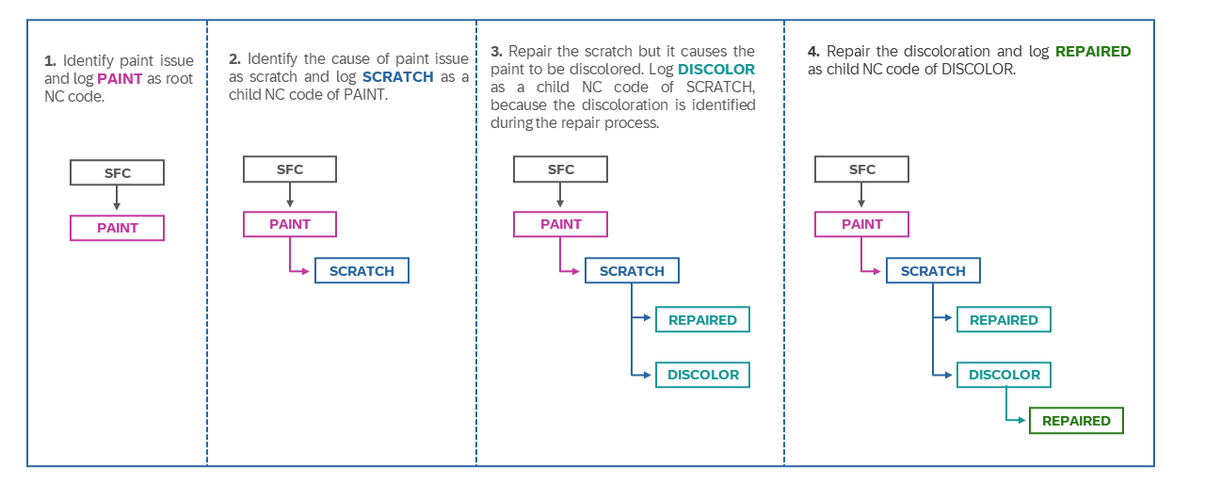
Example Scenario
Imagine a scenario where a painted product has a scratch. The primary NC code could be "PAINT," while "SCRATCH" and "DISCOLOR" could serve as secondary codes. This hierarchy helps in identifying the root cause and the necessary corrective actions. Once the scratch is repaired, a "REPAIRED" code could serve as the corrective action and automatically close all the other nonconformances codes captured above it. See diagram below:
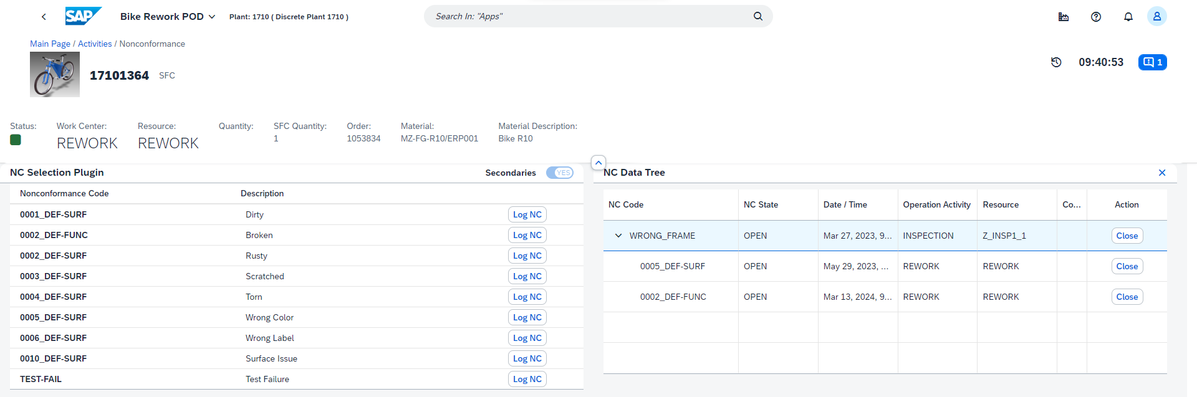
This is how it looks like in PODs (Production Operator Dashboards), the worker UIs:
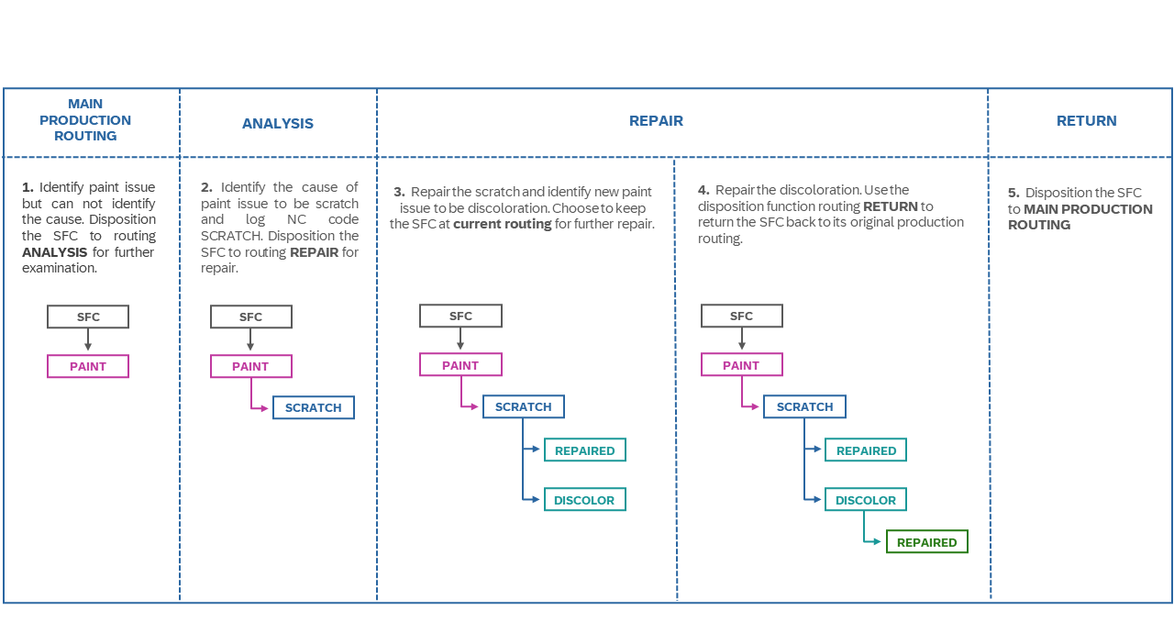
Disposition Routings
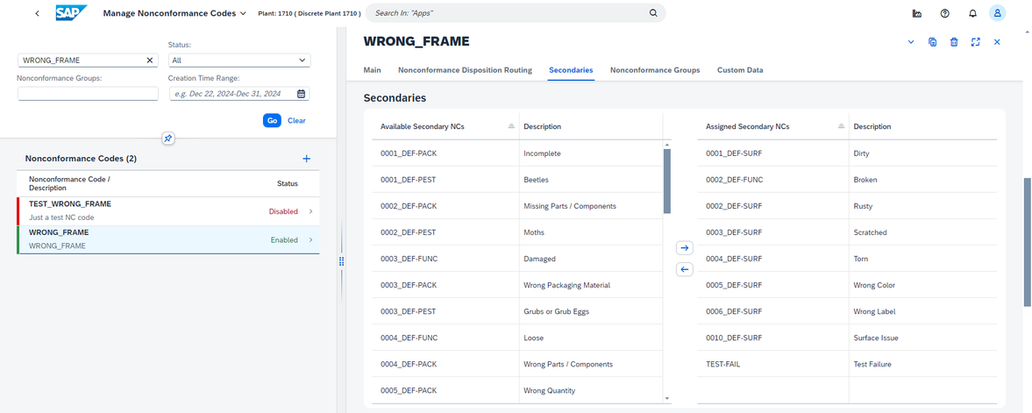
In complex manufacturing environments, specific routings may be required to handle nonconformances effectively. In SAP Digital Manufacturing, these routings can be assigned to NC codes, so workers can disposition SFCs a nonconformance (NC) disposition routing just by logging a nonconformance. Whether it's analysis, repair, or return, disposition routings streamline the handling process. See diagram below:
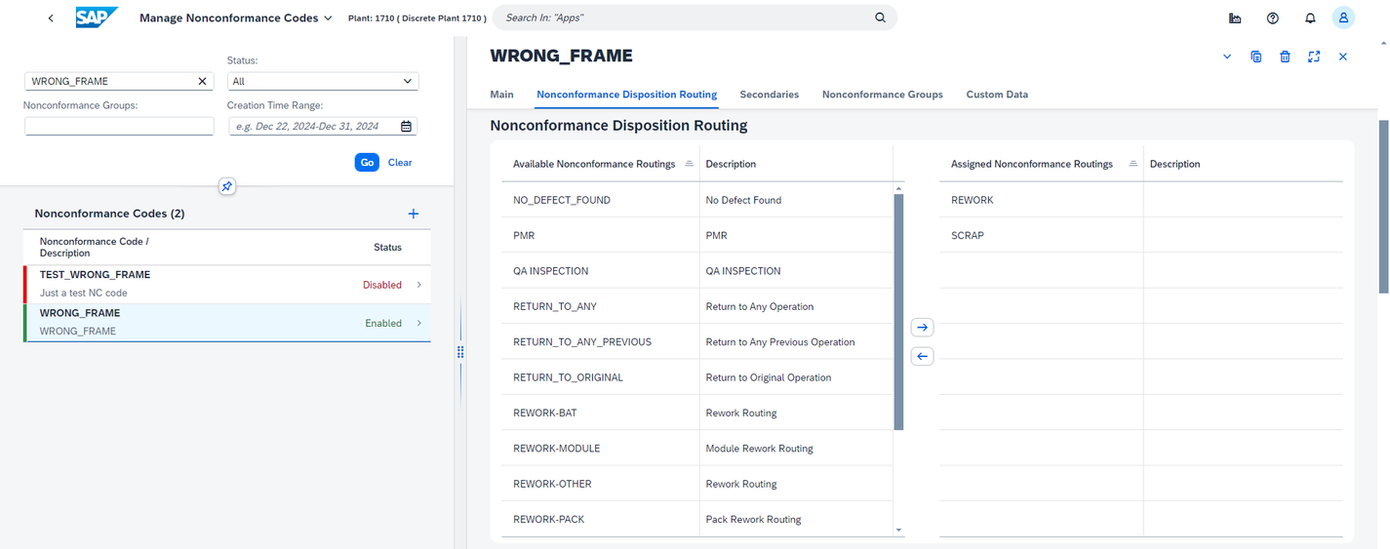
Nonconformance Disposition Routings can be assigned to individual nonconformance codes in Manage Nonconformance Codes app, as shown below, where 'REWORK' and 'SCRAP' routings are attached to 'WRONG_FRAME' NC code:
Recording Additional Data
Beyond standard information, certain nonconformances may require additional data for thorough analysis. By assigning a data type to an NC code, manufacturers can capture relevant details such as location and repairability. This customizable approach ensures that all pertinent information is recorded for comprehensive problem-solving.
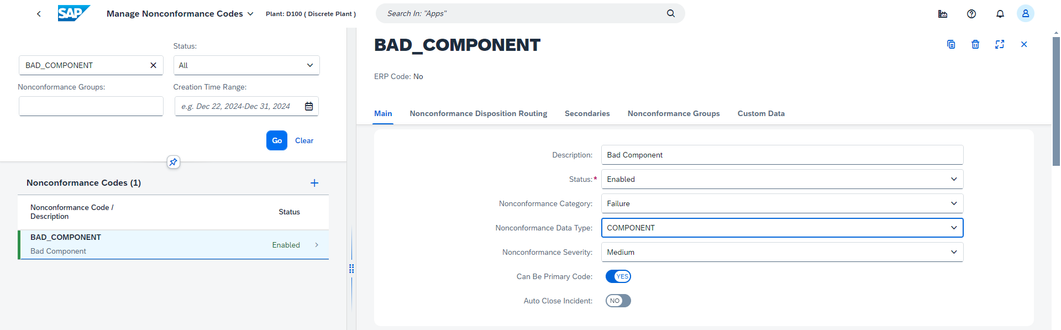
In the example below, 'COMPONENT' Nonconformance Data Type is assigned to 'BAD_COMPONENT' NC code:
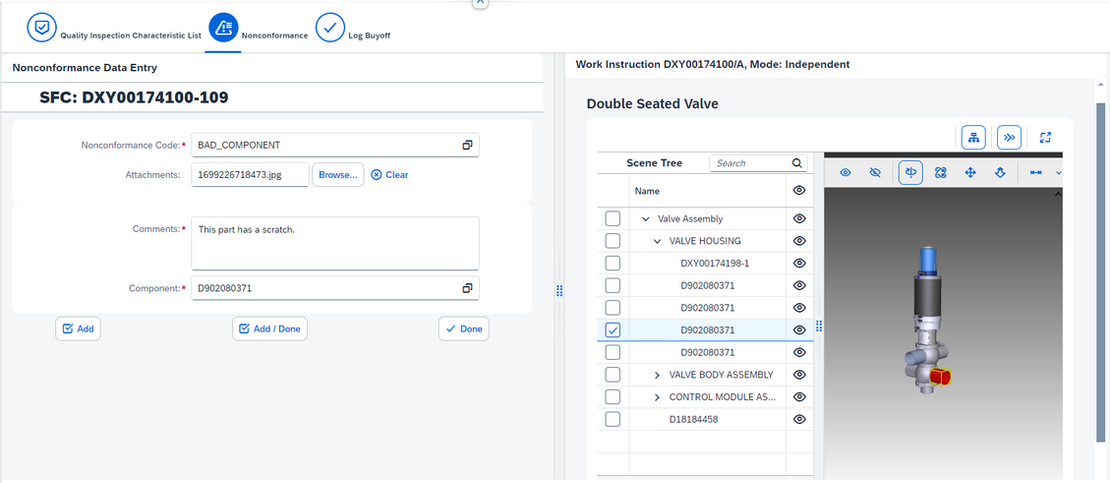
So, when 'BAD_COMPONENT' NC code is logged, extra data fields like attachments, comments and component location are shown:
Analytics
Nonconformance codes serve as the building blocks for detailed analytics in manufacturing processes. By categorizing and hierarchically organizing nonconformances, these codes provide a structured framework for analyzing production issues.
Each code represents a specific type of nonconformance, allowing for granular data collection and analysis. With the ability to record additional information, such as root cause analysis and repair status, Nonconformance Codes enable comprehensive insight into the factors contributing to quality deviations.
By leveraging this rich dataset, manufacturers can identify trends, pinpoint recurring issues, and implement targeted corrective actions to continuously improve product quality and operational efficiency. In essence, Nonconformance Codes are not just tools for documenting deviations—they are powerful instruments for driving data-driven decision-making and continuous improvement initiatives in manufacturing.
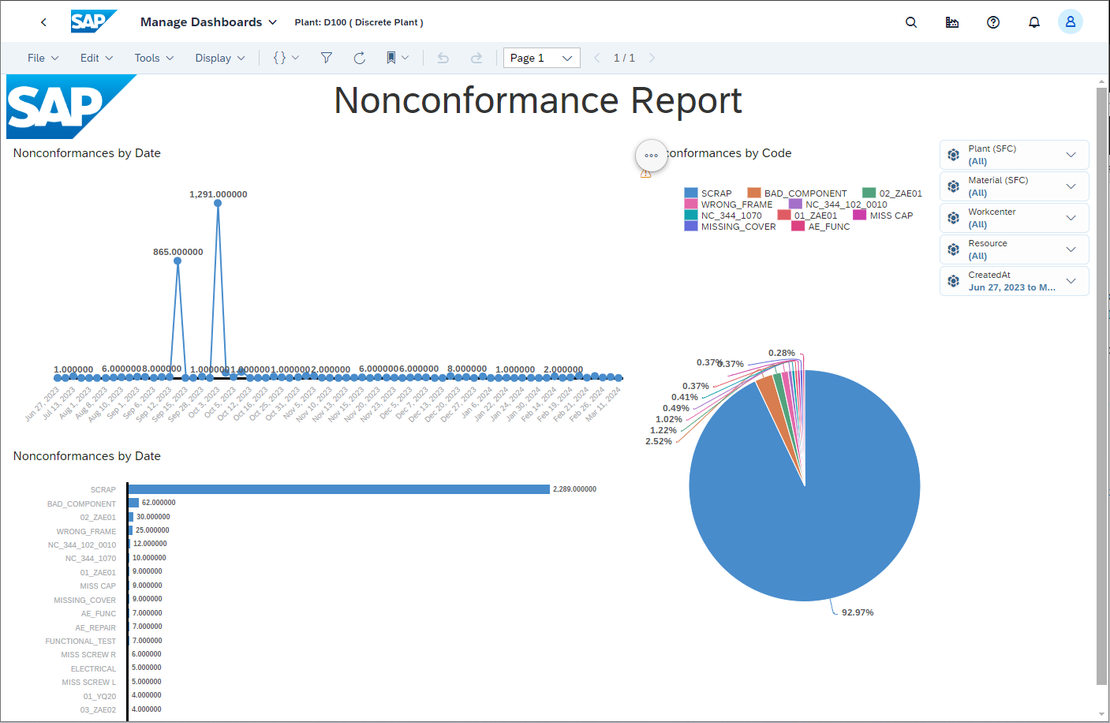
See below a simple Nonconformance Reported, created in SAP Digital Manufacturing leveraging Embedded SAC (SAP Digital Analytics Cloud) capabilities:
Benefits of NC Codes
- Streamlined Process: NC codes provide a standardized method for documenting nonconformances, reducing ambiguity and improving efficiency.
- Granular Analysis: The hierarchical structure allows for in-depth analysis of nonconformance data, facilitating root cause identification and corrective action.
- Customization: From categorization to data recording, NC codes offer flexibility to tailor the system according to specific manufacturing needs.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: By linking disposition routings to NC codes, operators can make informed decisions on the appropriate handling of nonconformances, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity.
Demo Videos
- Nonconformance POD in SAP Digital Manufacturing
- Capturing Data Fields when logging Nonconformances
- Barcode parsing and Nonconformances using 3d Work Instructions
Conclusion
Nonconformance codes play a vital role in maintaining product quality and operational excellence in manufacturing. By leveraging SAP Digital Manufacturing's robust capabilities for NC code management, organizations can effectively address nonconformances, drive continuous improvement, and deliver superior products to customers.
Experiencing SAP Digital Manufacturing
You can have a glimpse and experience several aspects of SAP Digital Manufacturing via the Interactive Value Journeys below:
Do you like this post? Please let me know in the comments section what you think. Any feedback is highly appreciated. Or, if you have any questions, please check SAP Community Q&A Area, or comment down below.
Thanks,
Manoel Costa
- SAP Managed Tags:
- SAP Digital Manufacturing
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
Business Trends
169 -
Business Trends
24 -
Catalog Enablement
1 -
Event Information
47 -
Event Information
5 -
Expert Insights
12 -
Expert Insights
47 -
intelligent asset management
1 -
Life at SAP
63 -
Product Updates
500 -
Product Updates
68 -
Release Announcement
1 -
SAP Digital Manufacturing for execution
1 -
Super Bowl
1 -
Supply Chain
1 -
Sustainability
1 -
Swifties
1 -
Technology Updates
187 -
Technology Updates
18
- Can’t Miss Asset and Service Management Sessions at SAP Sapphire 2024 in Orlando in Supply Chain Management Blogs by SAP
- Configure Weigh and Dispense (W&D) in SAP Digital Manufacturing using the new Asset Model (DMAM) in Supply Chain Management Blogs by SAP
- SAP Digital Manufacturing Interactive Value Journeys (IVJs) in Supply Chain Management Blogs by SAP
- SAP Digital Manufacturing 24.05 Release Highlights in Supply Chain Management Blogs by SAP
- Handling Speed Losses in SAP Digital Manufacturing in Supply Chain Management Blogs by SAP
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 8 | |
| 6 | |
| 5 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 3 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 |