
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Technology
- Technology Blogs by Members
- The What Is... The Why To... The How To... of: ...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
What is ESG ?
ESG is "Environmental, Social, and corporate Governance" and revolves around how well an Organisation is performing across these three pillars. The stronger an Organisation is across these pillars, the higher the Organisation's ESG score or rating will be.
What is an ESG score/rating ? For me it's like when I go on Booking.com or AirBnB to find an apartment or hotel for a family holiday, I am looking for the properties which have the highest rating. This is how it is with ESG, the ESG score shows the Organisation's rating across these dimensions, "Environmental, Social, and corporate Governance", where we would expect, the higher the score, the more we can trust the Organisation.
And ESG is more than that, as @James_Marland describes in the blog Your Ledger is about to go Green the European Union is on a journey bringing legislation and "are going to ask companies to maintain a second set of books, that run in parallel to the traditional ledgers, and that’s a set of books called the Green Ledger".
ESG scoring takes a holistic view of the Organisation:
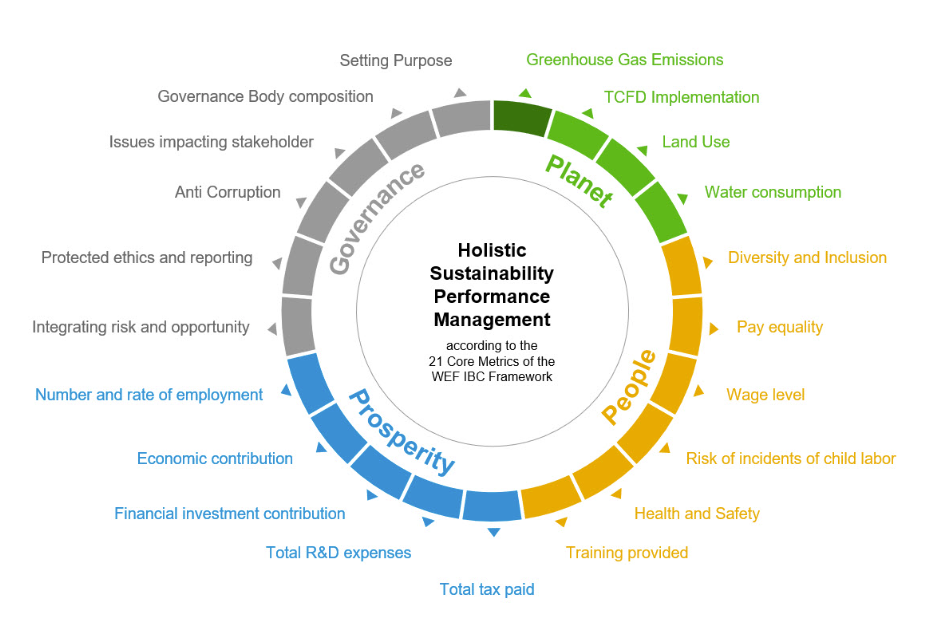
[thanks to @gunther_rothermel and his ESG Performance Management blog]
For me,
ESG is about Data.
Why to do ESG ?
There are hard reasons and softer reasons, the softer reasons are elaborated in more detail below, but the hard reason for doing ESG, the reason we cannot be avoided, is European legislation, and to repeat, so that we don't miss it, as @James_Marland describes in the blog Your Ledger is about to go Green the European Union is on a journey bringing legislation and "are going to ask companies to maintain a second set of books, that run in parallel to the traditional ledgers, and that’s a set of books called the Green Ledger".
ESG (“Environmental, Social, and corporate Governance”) concerns are playing a greater role in investment decisions and hence corporate decision making.
Part of the ESG framework is scoring Organisations to measure how they are performing against ESG standards.
ESG scoring helps to provide a standardized way to quantify an Organisation’s ESG impact, and is consumed by:
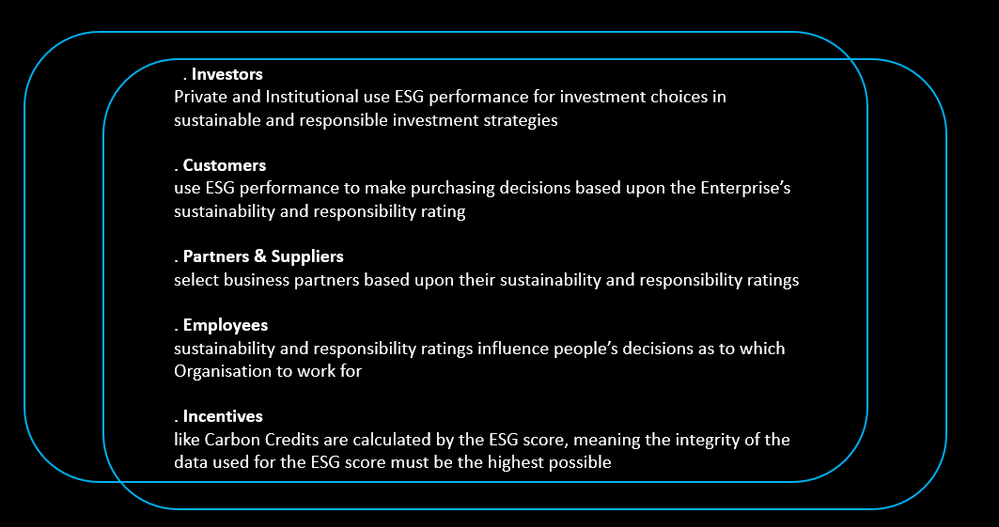
In her blog, @annchristinschechter , the report describes it like this:
The Situation: Sustainable Business is the 3rd Wave of Global Economic Transformation
Investors, shareholders, regulators, and consumers all demand responsibly derived products
and services with a smaller environmental footprint. Reducing global emissions,
waste, and social injustice requires a full-lifecycle approach with enterprises at the forefront.

Going back to the, Booking.com or AirBnB to find an apartment or hotel for a family holiday analogy, in the same way as a properties with lower ratings attract less interest, the time will soon be upon us when Organisations with lower ESG scores will be at a disadvantage compared to those with higher scores.
That and social responsibility is Why To Do ESG.
For me, again,
ESG is about the Data, and if the Data is so important, then we need to be able to Trust the Data.
How to do SAP, ESG, and Enterprise Blockchain
The ESG score is an example of the circular economy. The key to the score is the Data, the Data coming from in most cases the Edge, from Sensors and Things. As shown in the picture below, the Data from the Edge needs to be stored safely and securely so that it can be processed by the SAP Sustainability Control Tower:
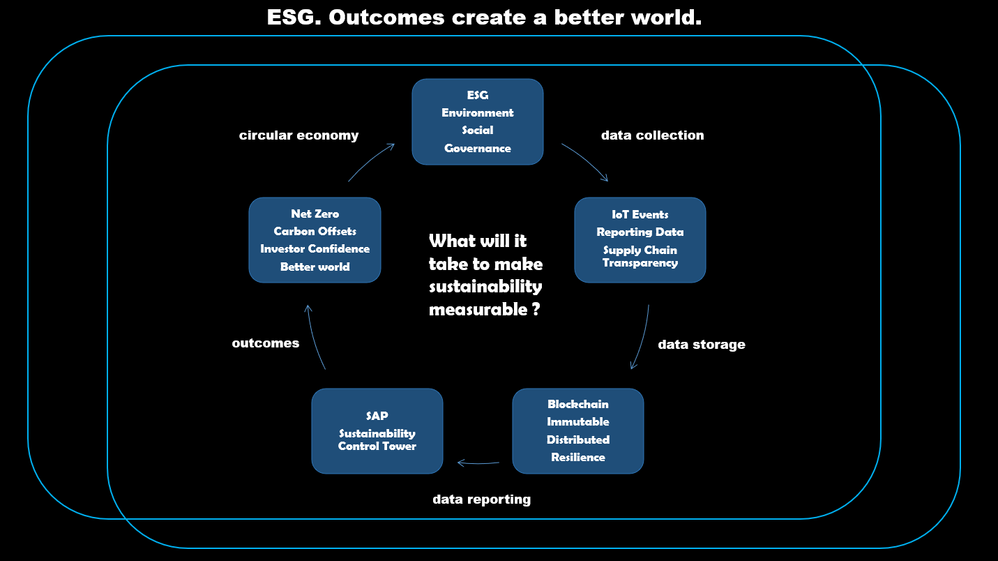
SAP by the way, have a portfolio of Products to enable Enterprises to do ESG, and these include:
. SAP Sustainability Footprint Management
. SAP Sustainability Data Exchange
. SAP Sustainability Control Tower
In this blog we are focusing on protecting the integrity and originality and confidentiality of Data which is used to do ESG scoring and rating, Data which would then be consumed by for example the SAP Sustainability Control Tower.
There are two related challenges to overcome when collecting data for ESG scoring. The first comes in two parts: simply collecting the data in the first place, since there may be large numbers of sensors and systems (consider carbon emissions across a supply chain, and the myriad vehicles, vessels, machines and people involved); and moving that data fast enough that decisions can be made using it (which we’ll use as the definition of “real-time” in the rest of this blog)
The second challenge is that with any measurement system, the measurement is only as reliable as the data collected. This opens a “trust gap:” organisations have incentives to increase their ESG score: how can we be sure of the validity of the data they’ve collected? Similarly, how can they be sure of the data their subcontractors have collected?
Investors are increasingly demanding ESG Audits of target Organisations, and it’s likely the requirements of ESG scoring become stricter. Being able to demonstrate that an Organisation’s ESG data collection methods are beyond reproach is likely to represent a significant business advantage, along with benefits of reacting to this data in real time.
ESG Data Sources
ESG measurement data can contain Personal Sensitive and Business Critical information across the Corporate domains of:
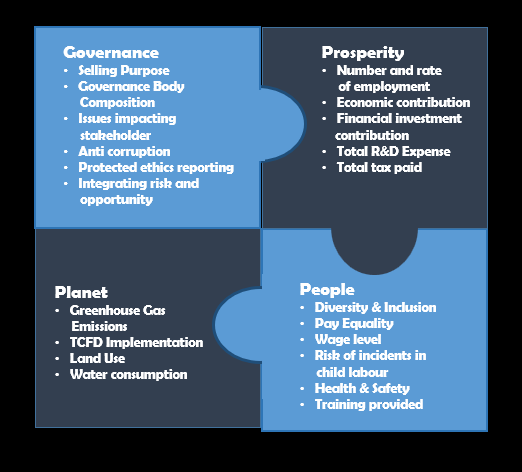
Data sources for this data come from all over the organisation: Enterprise Applications and Things (sensors, monitors and connected applications at the edge), including ERP systems, HR systems, Sensors measuring CO2 levels and Water Quality.
In this blog we’ll take as an example data from Waste Trucks proving responsible disposal of Corporate waste, to see just how many sources of data there are and how to address the challenges this creates.
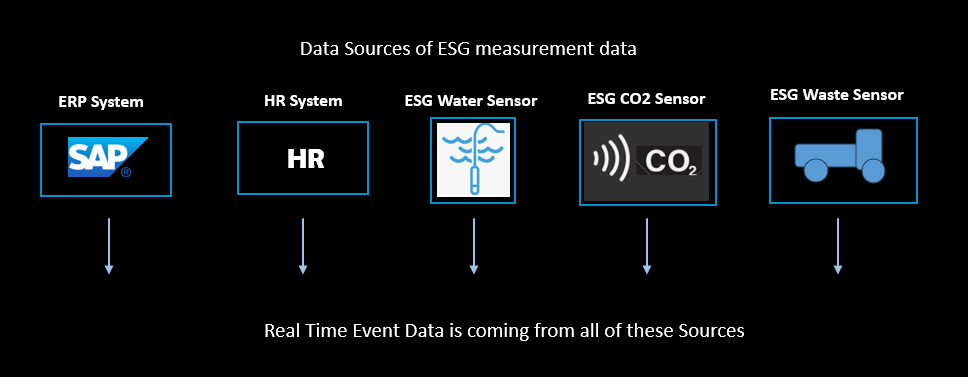
ESG Data Security
In terms of the NIST CIA Triad for Data Security, Criticality, Integrity, Availability, ESG measurement data comes in Very High across all three classifications.
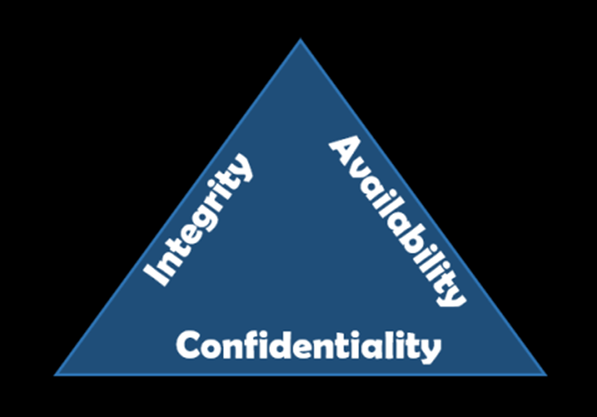
As the ESG performance rating is so critical, data measurements which are used need to be auditable and the integrity of the data completely trustworthy, so the highest level of data security and integrity protection is required.
To address the “trust-gap”, it is essential that it can be proven that the ESG measurement data cannot be interfered with and can be trusted. At the same time, the ESG measurement data needs to be available to a number of Enterprise Applications for it to make any actionable change.
Enterprise Architecture saves the day...
So, this is where Enterprise IT comes in to save the day and solve the problem.
The business requirement is for:
. Data from any source needs to be Stored as close to the source of the Data as possible
. The source of the Data can be Edge / IoT / Mobile Things, and can also be ERP and Enterprise Software Applications
. The Data needs to be stored with the highest level of integrity and originality and confidentiality and sensitivity protection
. The Data store solution should be available out of the box in a commercial off the shelf product
. The Data must be stored Immutably
As discussed in the previous blog, [SAP Enterprise Architecture: Positioning Blockchain Database as an Enterprise Technology Standard 🚀] when we look in to our Enterprise Architecture Technology Standards we see there is only 1 Technology Standard in the Enterprise which is positioned with the capabilities to fulfill all of those requirements out of the box, and that is the, Enterprise Blockchain Platform and Enterprise Blockchain Databases.
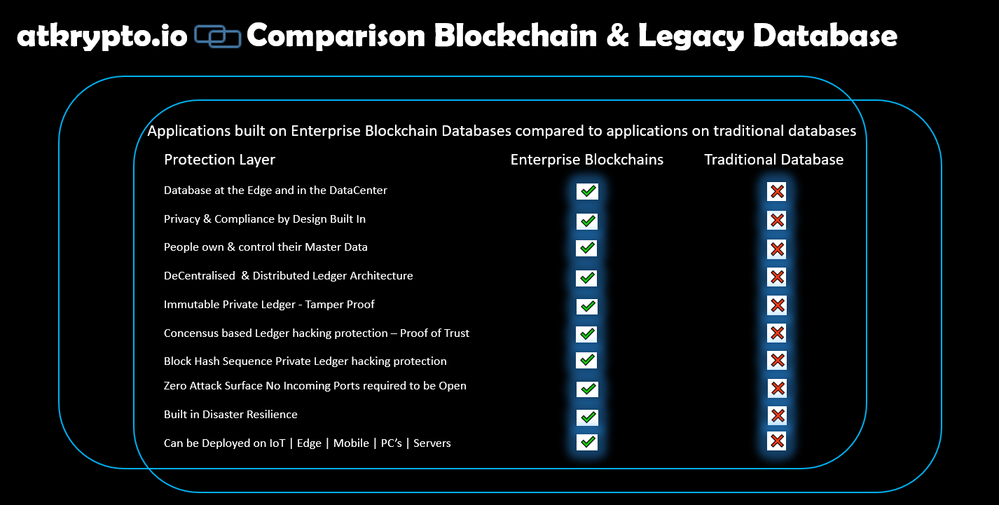
Why Enterprise Blockchain Database for securely storing ESG measurement data ?
As we described in the first blog in this series, [Why I love SAP and Blockchain Databases and why you should too 🚀], there are four characteristics which make Blockchain natively the most secure data storage.
These are:

A Blockchain can only be called a Blockchain if it has these characteristics, the point being that once data is entered in a blockchain it cannot be altered or deleted. This provides trust in the data, so that, for instance, ESG auditors know that if a measurement is calculated from data held in a Blockchain, they can trust that the data hasn’t been adulterated while being stored.
In the following Enterprise Blockchain Platform for ESG deployment example scenarios we have data coming from multiple data sources, some of which are at the Edge/IoT and some are Enterprise Applications in the DataCenter or Cloud. At the same time data which is being written to the Enterprise Blockchain Database can originate from multiple Organisations which are sharing the same Enterprise Blockchain Platform and Database as a common shared single source of truth.
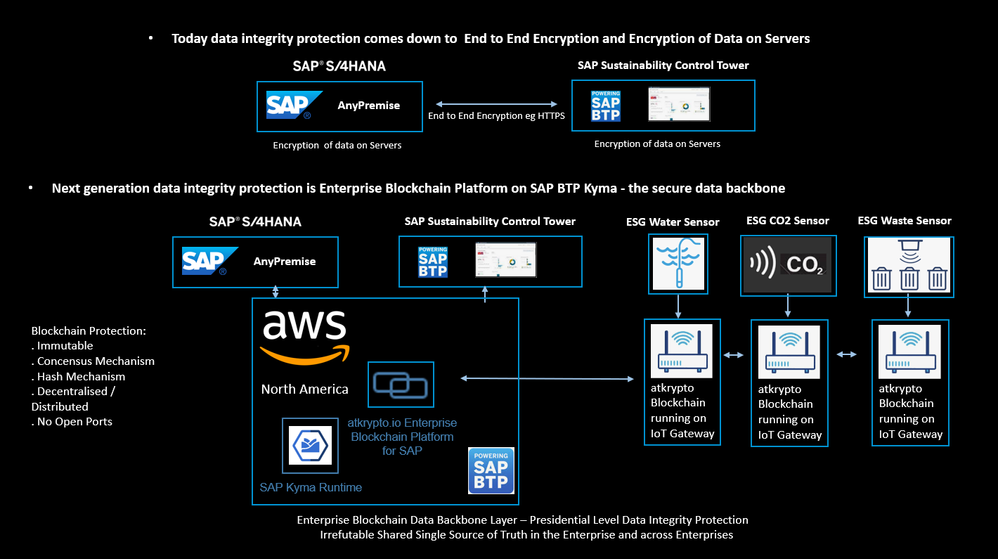
The immutability of blockchain data is what enables trust between what otherwise might be competing organisations.
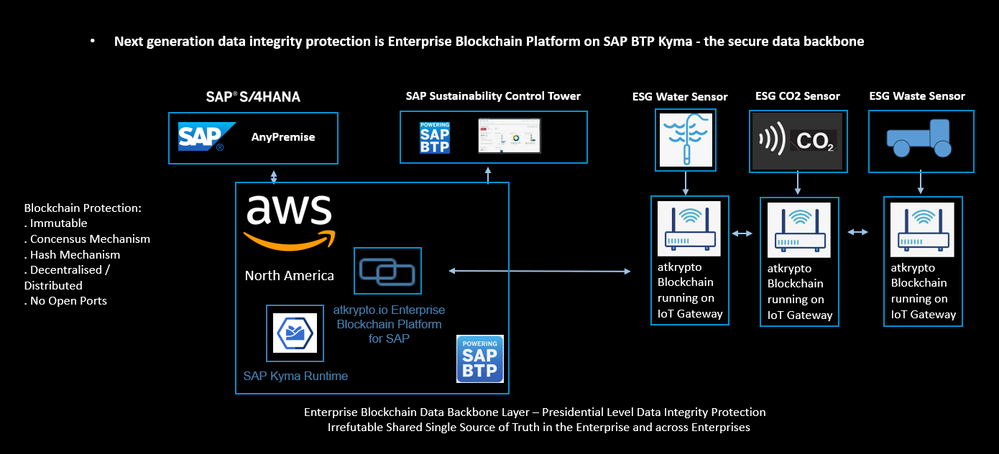
Example 1, Single Enterprise Blockchain Database within your Organisation for ESG Data
In this example, an Enterprise is storing ESG data to its Enterprise Blockchain Platform.
ESG data is originating from multiple sources as shown in the diagram:
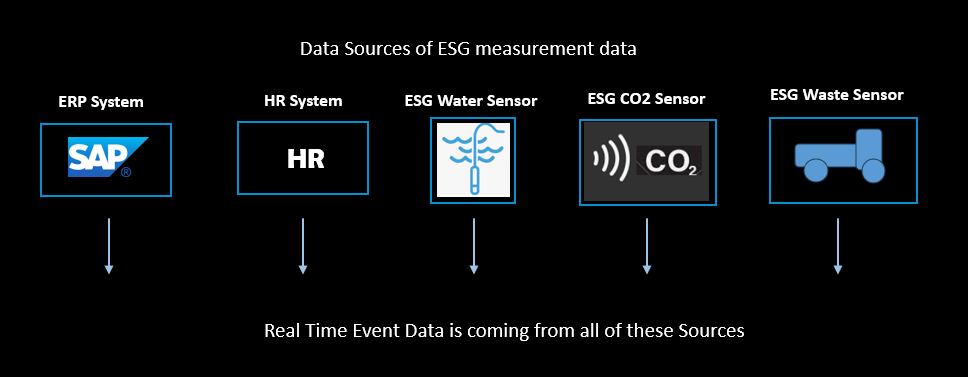
Imagine an Enterprise subcontracting the disposal of its electronic waste. For ESG compliance the Enterprise needs to make sure that its waste carrying vehicles aren’t tempted to take short cuts in personnel management or the disposal, but must also verify the subcontractor is upholding their standards, too.
Data can be used from the Waste Truck’s GPS and onboard cameras to prove both where the waste was disposed of geographically through the GPS data and physically through the photographic evidence from the Truck’s on board cameras. Think about how delivery drivers photograph where they’ve left a parcel.
The collection of this data is enabled either by SAP Advanced Event Mesh, which spans geographies and environments such as On-Premise, Cloud and all the way to the Edge, connecting the Waste Truck to Enterprise Applications such as Route Planning, HR management, Scheduling and other operational systems as well as the Enterprise Blockchain Database Edge Tenants and the Enterprise Blockchain Database Server Tenants.
All this data, including the photographs, are stored on the Enterprise Blockchain Platform Database, the photographs will be stored as Enterprise NFT’s in the Enterprise Blockchain Wallet.
Example 2, Single Blockchain shared across Organisations for ESG Data
This example is where the real beauty of the Distributed Ledger Technology is brought in to focus.
Enterprise Blockchain Platform Database as a shared single source of truth across Organisations.
In this example the Enterprise Blockchain Platform is running Blockchain Database Tenants in your Organisation and also in your Partner Organisations. This enables the Enterprise Blockchain Database to provide an irrefutable shared single source of truth for data across Organisations, who normally would not openly trust each other with data.
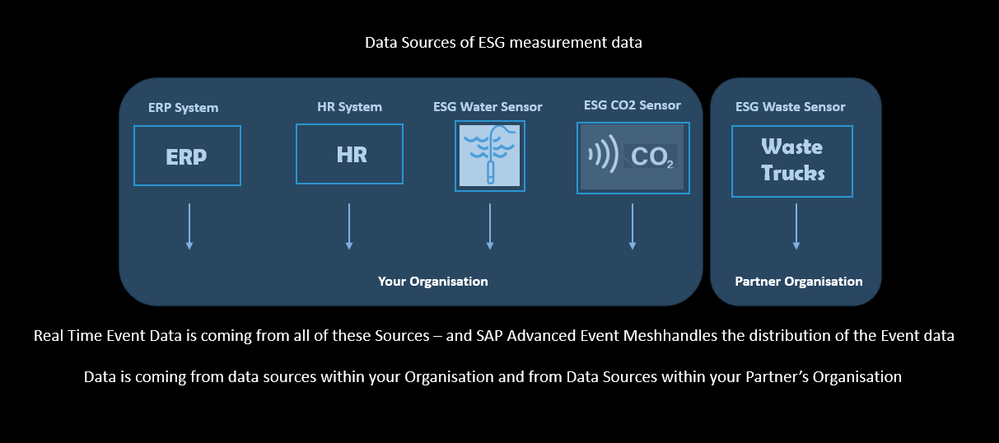
Your Organisation outsources industrial waste collection and responsible disposal to a 3rd party Organisation.
Your ERP system orders the 3rd Party Waste Processor to collect and dispose of industrial waste.
For your Organisation’s ESG data, you depend upon evidence that the 3rd Party Organisation is responsibly disposing of the waste.
The Enterprise Blockchain Platform Database enables a shared single source of truth to be created across the Organisations by running inter-connected Blockchain Server Nodes in both Organisations.
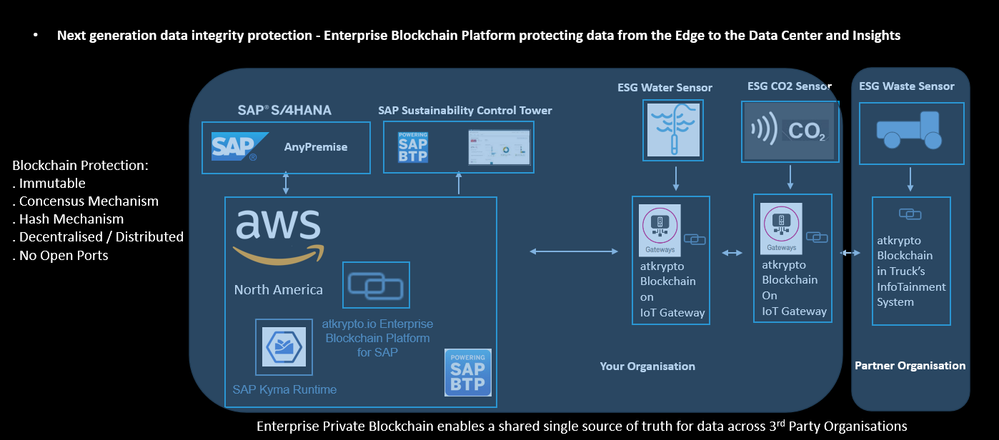
In the above example, the Enterprise Blockchain Platform Database is running across Organisations.
Your Organisation is writing data to the same Enterprise Blockchain Database as your 3rd Party partner Organisation.
The Enterprise Blockchain Database contains evidence from your S/4HANA ERP system that the 3rd Party Waste Processor was ordered to process your industrial waste.
In the same Enterprise Blockchain Database the 3rd Party Waste Disposal Organisation is storing evidence from the Waste Trucks that the waste was collected from your premises and disposed of responsibly at the authorised waste treatment center.
This scenario opens a new world of opportunities for multiple Enterprises to share data, multi-Enterprise collaboration, with the Enterprise Blockchain as the irrefutable common shared single source of truth across Organisations.
The most beautiful thing about the picture above is that we have an Enterprise Blockchain Database shared across 3rd party Organisations, this achieves a few things:
. Saves a huge amount of effort to integrate the IT systems of the two 3rd party Organisations
. Enables both Organisations to write Data to the same Enterprise Blockchain Database
. Enables both the ESG Customer Organisation to read the Data from the Enterprise Blockchain Database into their SAP Sustainability Control Tower to enable ESG Reporting
. Enables both Organisations to be able to trust the Data in the Enterprise Blockchain Database
. Enables both Organisations to know that neither Organisation can modify the Data in the Enterprise Blockchain Database
. Enables both Organisations to know that their shared Data is being protected to the highest level natively out of the box of any Database Product
Wrapping Up
To wrap up, a simple reminder,
The Digital Transformation of Information Security is Enterprise Blockchain
Enterprise Blockchain is the Next Generation Data Integrity, Originality, Confidentiality Protection
Enterprise Blockchain, Enterprise Distributed Ledger Technology is re-imagining information security
With regards to ESG,
ESG is about Data
ESG is about the Data, and if the Data is so important, then we need to be able to Trust the Data
If we need to be able to Trust the Data, then we need to put it on to the Enterprise Blockchain as the irrefutable common shared single source of truth across our Organisation and other Organisations
Enterprise Blockchain is both a Secure Store and a Secure Communication Channel.
This blog is the fifth in the series, the previous blogs are here, here, here and here.
We will be describing more use cases for this scenario in future blogs, including for example the Insurance use case, where the Carrier, the Broker, and the Customer are on the same Enterprise Blockchain.
As McKinsey & Company, in their December 2023 Featured Insights Publication, gave a beautiful description of what is unique and special about Blockchain, "Blockchain is a secure database shared across a network of participants, where up-to-date information is available to all participants at the same time".
The good news is, as we discussed in the previous blog, this is no longer hype, we can do all of this today, and now, within the SAP Partner Edge Open EcoSystem there are enabling technology Blockchain Products designed and built by SAP Experts specifically for the needs of SAP Customers to make doing Blockchain and SAP easy, and so you can do SAP and Blockchain, today it's real and there's nothing stopping you.
So what are we waiting for ? Oh yeah, more use cases, ok, that will continue in the next blog
What do you think, are the words Blockchain, Web3, Distributed Ledger Technology, starting to appear in your Company's visions and technology visions ? What use cases are you looking at ? Let's chat about it in the comments.
Credits: Tom Fairbairn Distinguished Engineer at Solace contributed to this blog. We will be following this blog up with a deeper Technical Architecture dive into getting the Data and how SAP Advanced Event Mesh is positioned in the Solution Architecture for publishing the real time ESG Data and Enterprise Blockchain is positioned for Protecting the ESG Data, Event Driven Blockchain, Publish & Protect.
For now, over and out. 🚀
Andy Silvey.
Independent SAP Technical Architect and CEO of atkrypto.io
Author Bio:
Andy Silvey is a 25 years SAP Technology veteran [15 years SAP Basis and 10 years SAP Tech Arch including Tech, Integration, Security, Data from 3.1H to S/4HANA PCE on RISE and the BTP and everything in between, and former SCN Moderator and Mentor alumni].
Andy is also co-Founder of atkrypto inc, an startup whose ambition is to make Blockchain easy for Enterprise.
atkrypto.io's flagship product is the atkrypto Enterprise Blockchain Platform for SAP, and atkrypto.io is a SAP Partner Edge Open EcoSystem Partner.
The atkrypto Enterprise Blockchain Platform for SAP has been designed by SAP Independent Experts for the needs of SAP Customers and to be deployed on the SAP BTP Kyma Runtime Service and leverage native integration to SAP Products.
atkrypto Enterprise Blockchain Platform for SAP has a number of unique qualities, including being the only Blockchain software in the world which has a DataCenter version and a light mobile version which can run on Edge/IoT/Mobile devices and enables data to be written to the Blockchain at the Edge where that same Blockchain is running on a Server in the DataCenter, protecting the integrity and originality of data from the Edge to Insights. Taking Blockchain to the Data at the Edge instead of taking the Data to the Blockchain.
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
"automatische backups"
1 -
"regelmäßige sicherung"
1 -
"TypeScript" "Development" "FeedBack"
1 -
505 Technology Updates 53
1 -
ABAP
14 -
ABAP API
1 -
ABAP CDS Views
2 -
ABAP CDS Views - BW Extraction
1 -
ABAP CDS Views - CDC (Change Data Capture)
1 -
ABAP class
2 -
ABAP Cloud
3 -
ABAP Development
5 -
ABAP in Eclipse
1 -
ABAP Platform Trial
1 -
ABAP Programming
2 -
abap technical
1 -
abapGit
1 -
absl
2 -
access data from SAP Datasphere directly from Snowflake
1 -
Access data from SAP datasphere to Qliksense
1 -
Accrual
1 -
action
1 -
adapter modules
1 -
Addon
1 -
Adobe Document Services
1 -
ADS
1 -
ADS Config
1 -
ADS with ABAP
1 -
ADS with Java
1 -
ADT
2 -
Advance Shipping and Receiving
1 -
Advanced Event Mesh
3 -
Advanced formula
1 -
AEM
1 -
AI
8 -
AI Launchpad
1 -
AI Projects
1 -
AIML
9 -
Alert in Sap analytical cloud
1 -
Amazon S3
1 -
Analytical Dataset
1 -
Analytical Model
1 -
Analytics
1 -
Analyze Workload Data
1 -
annotations
1 -
API
1 -
API and Integration
3 -
API Call
2 -
API security
1 -
Application Architecture
1 -
Application Development
5 -
Application Development for SAP HANA Cloud
3 -
Applications and Business Processes (AP)
1 -
Artificial Intelligence
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
5 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) 1 Business Trends 363 Business Trends 8 Digital Transformation with Cloud ERP (DT) 1 Event Information 462 Event Information 15 Expert Insights 114 Expert Insights 76 Life at SAP 418 Life at SAP 1 Product Updates 4
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise Oil Gas IoT Exploration Production
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise sustainability responsibility esg social compliance cybersecurity risk
1 -
ASE
1 -
ASR
2 -
ASUG
1 -
Attachments
1 -
Authorisations
1 -
Automating Processes
1 -
Automation
2 -
aws
2 -
Azure
1 -
Azure AI Studio
1 -
Azure API Center
1 -
Azure API Management
1 -
B2B Integration
1 -
Backorder Processing
1 -
Backpropagation
1 -
Backup
1 -
Backup and Recovery
1 -
Backup schedule
1 -
BADI_MATERIAL_CHECK error message
1 -
Bank
1 -
Bank Communication Management
1 -
BAS
1 -
basis
2 -
Basis Monitoring & Tcodes with Key notes
2 -
Batch Management
1 -
BDC
1 -
Best Practice
1 -
bitcoin
1 -
Blockchain
3 -
bodl
1 -
BOP in aATP
1 -
BOP Segments
1 -
BOP Strategies
1 -
BOP Variant
1 -
BPC
1 -
BPC LIVE
1 -
BTP
13 -
BTP AI Launchpad
1 -
BTP Destination
2 -
Business AI
1 -
Business and IT Integration
1 -
Business application stu
1 -
Business Application Studio
1 -
Business Architecture
1 -
Business Communication Services
1 -
Business Continuity
2 -
Business Data Fabric
3 -
Business Fabric
1 -
Business Partner
12 -
Business Partner Master Data
10 -
Business Technology Platform
2 -
Business Trends
4 -
BW4HANA
1 -
CA
1 -
calculation view
1 -
CAP
4 -
Capgemini
1 -
CAPM
1 -
Catalyst for Efficiency: Revolutionizing SAP Integration Suite with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and
1 -
CCMS
2 -
CDQ
12 -
CDS
2 -
Cental Finance
1 -
Certificates
1 -
CFL
1 -
Change Management
1 -
chatbot
1 -
chatgpt
3 -
CL_SALV_TABLE
2 -
Class Runner
1 -
Classrunner
1 -
Cloud ALM Monitoring
1 -
Cloud ALM Operations
1 -
cloud connector
1 -
Cloud Extensibility
1 -
Cloud Foundry
4 -
Cloud Integration
6 -
Cloud Platform Integration
2 -
cloudalm
1 -
communication
1 -
Compensation Information Management
1 -
Compensation Management
1 -
Compliance
1 -
Compound Employee API
1 -
Configuration
1 -
Connectors
1 -
Consolidation Extension for SAP Analytics Cloud
2 -
Control Indicators.
1 -
Controller-Service-Repository pattern
1 -
Conversion
1 -
Cosine similarity
1 -
cryptocurrency
1 -
CSI
1 -
ctms
1 -
Custom chatbot
3 -
Custom Destination Service
1 -
custom fields
1 -
Customer Experience
1 -
Customer Journey
1 -
Customizing
1 -
cyber security
4 -
cybersecurity
1 -
Data
1 -
Data & Analytics
1 -
Data Aging
1 -
Data Analytics
2 -
Data and Analytics (DA)
1 -
Data Archiving
1 -
Data Back-up
1 -
Data Flow
1 -
Data Governance
5 -
Data Integration
2 -
Data Quality
12 -
Data Quality Management
12 -
Data Synchronization
1 -
data transfer
1 -
Data Unleashed
1 -
Data Value
8 -
database tables
1 -
Dataframe
1 -
Datasphere
3 -
datenbanksicherung
1 -
dba cockpit
1 -
dbacockpit
1 -
Debugging
2 -
Defender
1 -
Delimiting Pay Components
1 -
Delta Integrations
1 -
Destination
3 -
Destination Service
1 -
Developer extensibility
1 -
Developing with SAP Integration Suite
1 -
Devops
1 -
digital transformation
1 -
Disaster Recovery
1 -
Documentation
1 -
Dot Product
1 -
DQM
1 -
dump database
1 -
dump transaction
1 -
e-Invoice
1 -
E4H Conversion
1 -
Eclipse ADT ABAP Development Tools
2 -
edoc
1 -
edocument
1 -
ELA
1 -
Embedded Consolidation
1 -
Embedding
1 -
Embeddings
1 -
Employee Central
1 -
Employee Central Payroll
1 -
Employee Central Time Off
1 -
Employee Information
1 -
Employee Rehires
1 -
Enable Now
1 -
Enable now manager
1 -
endpoint
1 -
Enhancement Request
1 -
Enterprise Architecture
1 -
ESLint
1 -
ETL Business Analytics with SAP Signavio
1 -
Euclidean distance
1 -
Event Dates
1 -
Event Driven Architecture
1 -
Event Mesh
2 -
Event Reason
1 -
EventBasedIntegration
1 -
EWM
1 -
EWM Outbound configuration
1 -
EWM-TM-Integration
1 -
Existing Event Changes
1 -
Expand
1 -
Expert
2 -
Expert Insights
2 -
Exploits
1 -
Fiori
15 -
Fiori Elements
2 -
Fiori SAPUI5
12 -
first-guidance
1 -
Flask
2 -
FTC
1 -
Full Stack
8 -
Funds Management
1 -
gCTS
1 -
GenAI hub
1 -
General
2 -
Generative AI
1 -
Getting Started
1 -
GitHub
9 -
Google cloud
1 -
Grants Management
1 -
groovy
1 -
GTP
1 -
HANA
6 -
HANA Cloud
2 -
Hana Cloud Database Integration
2 -
HANA DB
2 -
Hana Vector Engine
1 -
HANA XS Advanced
1 -
Historical Events
1 -
home labs
1 -
HowTo
1 -
HR Data Management
1 -
html5
8 -
HTML5 Application
1 -
Identity cards validation
1 -
idm
1 -
Implementation
1 -
Infuse AI
1 -
input parameter
1 -
instant payments
1 -
Integration
3 -
Integration Advisor
1 -
Integration Architecture
1 -
Integration Center
1 -
Integration Suite
1 -
intelligent enterprise
1 -
iot
1 -
Java
1 -
job
1 -
Job Information Changes
1 -
Job-Related Events
1 -
Job_Event_Information
1 -
joule
4 -
Journal Entries
1 -
Just Ask
1 -
Kerberos for ABAP
8 -
Kerberos for JAVA
8 -
KNN
1 -
Launch Wizard
1 -
Learning Content
2 -
Life at SAP
5 -
lightning
1 -
Linear Regression SAP HANA Cloud
1 -
Loading Indicator
1 -
local tax regulations
1 -
LP
1 -
Machine Learning
4 -
Marketing
1 -
Master Data
3 -
Master Data Management
14 -
Maxdb
2 -
MDG
1 -
MDGM
1 -
MDM
1 -
Message box.
1 -
Messages on RF Device
1 -
Microservices Architecture
1 -
Microsoft Universal Print
1 -
Middleware Solutions
1 -
Migration
5 -
ML Model Development
1 -
Modeling in SAP HANA Cloud
8 -
Monitoring
3 -
MTA
1 -
Multi-Record Scenarios
1 -
Multilayer Perceptron
1 -
Multiple Event Triggers
1 -
Myself Transformation
1 -
Neo
1 -
Neural Networks
1 -
New Event Creation
1 -
New Feature
1 -
Newcomer
1 -
NodeJS
3 -
ODATA
2 -
OData APIs
1 -
odatav2
1 -
ODATAV4
1 -
ODBC
1 -
ODBC Connection
1 -
Onpremise
1 -
open source
2 -
OpenAI API
1 -
Oracle
1 -
PaPM
1 -
PaPM Dynamic Data Copy through Writer function
1 -
PaPM Remote Call
1 -
Partner Built Foundation Model
1 -
PAS-C01
1 -
Pay Component Management
1 -
PGP
1 -
Pickle
1 -
PLANNING ARCHITECTURE
1 -
Popup in Sap analytical cloud
1 -
PostgrSQL
1 -
POSTMAN
1 -
Prettier
1 -
Process Automation
2 -
Product Updates
6 -
PSM
1 -
Public Cloud
1 -
Python
5 -
python library - Document information extraction service
1 -
Qlik
1 -
Qualtrics
1 -
RAP
3 -
RAP BO
2 -
Record Deletion
1 -
Recovery
1 -
recurring payments
1 -
redeply
1 -
Release
1 -
Remote Consumption Model
1 -
Replication Flows
1 -
research
1 -
Resilience
1 -
REST
1 -
REST API
1 -
Retagging Required
1 -
Risk
1 -
rolandkramer
1 -
Rolling Kernel Switch
1 -
route
1 -
rules
1 -
S4 HANA
1 -
S4 HANA Cloud
1 -
S4 HANA On-Premise
1 -
S4HANA
4 -
S4HANA Cloud
1 -
S4HANA_OP_2023
2 -
SAC
10 -
SAC PLANNING
9 -
SAP
4 -
SAP ABAP
1 -
SAP Advanced Event Mesh
1 -
SAP AI Core
9 -
SAP AI Launchpad
8 -
SAP Analytic Cloud Compass
1 -
Sap Analytical Cloud
1 -
SAP Analytics Cloud
4 -
SAP Analytics Cloud for Consolidation
3 -
SAP Analytics Cloud Story
1 -
SAP analytics clouds
1 -
SAP API Management
1 -
SAP BAS
1 -
SAP Basis
6 -
SAP BODS
1 -
SAP BODS certification.
1 -
SAP BTP
23 -
SAP BTP Build Work Zone
2 -
SAP BTP Cloud Foundry
7 -
SAP BTP Costing
1 -
SAP BTP CTMS
1 -
SAP BTP Generative AI
1 -
SAP BTP Innovation
1 -
SAP BTP Migration Tool
1 -
SAP BTP SDK IOS
1 -
SAP BTPEA
1 -
SAP Build
11 -
SAP Build App
1 -
SAP Build apps
1 -
SAP Build CodeJam
1 -
SAP Build Process Automation
3 -
SAP Build work zone
10 -
SAP Business Objects Platform
1 -
SAP Business Technology
2 -
SAP Business Technology Platform (XP)
1 -
sap bw
1 -
SAP CAP
2 -
SAP CDC
1 -
SAP CDP
1 -
SAP CDS VIEW
1 -
SAP Certification
1 -
SAP Cloud ALM
4 -
SAP Cloud Application Programming Model
1 -
SAP Cloud Integration for Data Services
1 -
SAP cloud platform
8 -
SAP Companion
1 -
SAP CPI
3 -
SAP CPI (Cloud Platform Integration)
2 -
SAP CPI Discover tab
1 -
sap credential store
1 -
SAP Customer Data Cloud
1 -
SAP Customer Data Platform
1 -
SAP Data Intelligence
1 -
SAP Data Migration in Retail Industry
1 -
SAP Data Services
1 -
SAP DATABASE
1 -
SAP Dataspher to Non SAP BI tools
1 -
SAP Datasphere
9 -
SAP DRC
1 -
SAP EWM
1 -
SAP Fiori
3 -
SAP Fiori App Embedding
1 -
Sap Fiori Extension Project Using BAS
1 -
SAP GRC
1 -
SAP HANA
1 -
SAP HANA PAL
1 -
SAP HANA Vector
1 -
SAP HCM (Human Capital Management)
1 -
SAP HR Solutions
1 -
SAP IDM
1 -
SAP Integration Suite
9 -
SAP Integrations
4 -
SAP iRPA
2 -
SAP LAGGING AND SLOW
1 -
SAP Learning Class
1 -
SAP Learning Hub
1 -
SAP Master Data
1 -
SAP Odata
2 -
SAP on Azure
2 -
SAP PAL
1 -
SAP PartnerEdge
1 -
sap partners
1 -
SAP Password Reset
1 -
SAP PO Migration
1 -
SAP Prepackaged Content
1 -
SAP Process Automation
2 -
SAP Process Integration
2 -
SAP Process Orchestration
1 -
SAP Router
1 -
SAP S4HANA
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud for Finance
1 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud private edition
1 -
SAP Sandbox
1 -
SAP STMS
1 -
SAP successfactors
3 -
SAP SuccessFactors HXM Core
1 -
SAP Time
1 -
SAP TM
2 -
SAP Trading Partner Management
1 -
SAP UI5
1 -
SAP Upgrade
1 -
SAP Utilities
1 -
SAP-GUI
8 -
SAP_COM_0276
1 -
SAPBTP
1 -
SAPCPI
1 -
SAPEWM
1 -
sapfirstguidance
2 -
SAPHANAService
1 -
SAPIQ
1 -
sapmentors
1 -
saponaws
2 -
saprouter
1 -
SAPRouter installation
1 -
SAPS4HANA
1 -
SAPUI5
5 -
schedule
1 -
Script Operator
1 -
Secure Login Client Setup
8 -
security
9 -
Selenium Testing
1 -
Self Transformation
1 -
Self-Transformation
1 -
SEN
1 -
SEN Manager
1 -
service
1 -
SET_CELL_TYPE
1 -
SET_CELL_TYPE_COLUMN
1 -
SFTP scenario
2 -
Simplex
1 -
Single Sign On
8 -
Singlesource
1 -
SKLearn
1 -
Slow loading
1 -
soap
1 -
Software Development
1 -
SOLMAN
1 -
solman 7.2
2 -
Solution Manager
3 -
sp_dumpdb
1 -
sp_dumptrans
1 -
SQL
1 -
sql script
1 -
SSL
8 -
SSO
8 -
Substring function
1 -
SuccessFactors
1 -
SuccessFactors Platform
1 -
SuccessFactors Time Tracking
1 -
Sybase
1 -
system copy method
1 -
System owner
1 -
Table splitting
1 -
Tax Integration
1 -
Technical article
1 -
Technical articles
1 -
Technology Updates
15 -
Technology Updates
1 -
Technology_Updates
1 -
terraform
1 -
Threats
2 -
Time Collectors
1 -
Time Off
2 -
Time Sheet
1 -
Time Sheet SAP SuccessFactors Time Tracking
1 -
Tips and tricks
2 -
toggle button
1 -
Tools
1 -
Trainings & Certifications
1 -
Transformation Flow
1 -
Transport in SAP BODS
1 -
Transport Management
1 -
TypeScript
3 -
ui designer
1 -
unbind
1 -
Unified Customer Profile
1 -
UPB
1 -
Use of Parameters for Data Copy in PaPM
1 -
User Unlock
1 -
VA02
1 -
Validations
1 -
Vector Database
2 -
Vector Engine
1 -
Vectorization
1 -
Visual Studio Code
1 -
VSCode
2 -
VSCode extenions
1 -
Vulnerabilities
1 -
Web SDK
1 -
work zone
1 -
workload
1 -
xsa
1 -
XSA Refresh
1
- « Previous
- Next »
- revamped SAP First Guidance Collection in Technology Blogs by Members
- SAP Datasphere News in April in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Third-Party Cookies and SAP Analytics Cloud in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Break Down Departmental Silos with SAP's Consensus Net Revenue Planning Content in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Second time a Leader in the Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Process Mining in Technology Blogs by SAP
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 6 | |
| 5 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 |