- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- CRM and Customer Experience
- CRM and CX Blogs by SAP
- Power of E-commerce Subscription Models in Increas...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Introduction
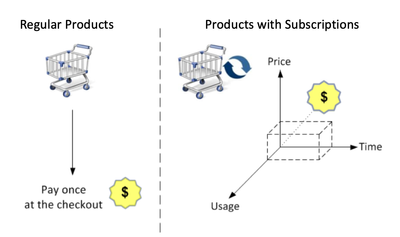
The subscription commerce business model involves customers paying recurring fees to receive products or services or bundles on a regular interval basis.
SAP Commerce Subscription feature is designed to simplify the process of managing recurring revenue streams and nurturing long-term customer relationships. In this blog, we'll explore what are the different subscription models and how SAP Commerce Subscriptions work, and the benefits they offer to B2B and B2C business models.
Business benefits
Subscription helps business team with the following benefits.
Improve Customer Experience - Customers will have a flexibility on choosing to select the products/ services or bundles which suits them and place the subscription order.
Increase revenue - Businesses can unlock predictable revenue streams in addition to regular one-time orders. This enables better financial planning and long-term growth strategies.
Increased loyalty / Customer Lifetime Value - Through ongoing value and personalized experiences, businesses can strengthen relationships and increase customer lifetime value and loyalty.
Operational efficiency - Subscriptions automate order placement, fulfilment from billing and invoicing and improve overall efficiency.
Type of subscriptions
For buyers to purchase regularly, they need the option that is the fastest and most convenient. It is also important that they have the flexibility to buy products and services according to their preferences and to change whenever they wish. The answer to the customer expectation is subscription commerce.
Volume-Usage Based Subscription
Using the guided selling approach, customers purchase exclusive content through personalized bundle options. Some examples are:
- Different types of media, like news, music, Software as a Service (SaaS), or software upgrades for downloadable packages
- B2B Customers subscribe to training courses, service plans, technical support etc.
- Telcos subscribe customers to a variety of service plans, bundling them with subsidized smartphones.
- Newspapers are following suit by offering a subscription to online editions.
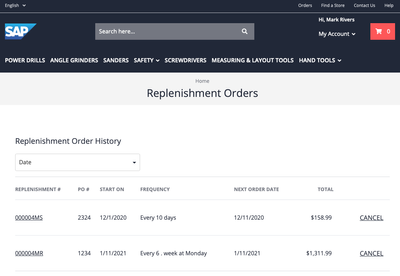
Replenishment subscriptions (Scheduled Orders)
Subscribers sign up for regularly recurring deliveries of a specific list of products that are used frequently and get billing paid periodically. Some examples are:
- Customers buy a list of groceries/household supplies regularly by scheduling fixed orders in the online store.
- Buying medicines/vitamins/lenses regularly from a pharmacy store. `
Customer Journey - Discovery phase
- When planning subscription commerce, the business team should consider the following factors:
- What kind of subscription model fits the business?
- How does the end-to-end business process of the subscription model work?
- Which of our products/services are best suited to a subscription model?
- What will be the pricing structure?
- What resources will be required to manage subscriptions, including fulfilment, customer service, and billing?
- Fit gap analysis with SAP Commerce and SAP Subscription billing and entitlement
- How willing are customers to commit to a subscription-based purchasing model?
How Subscription Commerce works
SAP Commerce Subscriptions enable businesses to offer subscription-based products and services to customers. Whether it's monthly delivery of essential goods, access to premium content, or ongoing support and maintenance. It provides the front-end customer experience features, back-office administration and also supports integration with the infrastructure needed to manage recurring billing, automate order processing.
Replenishment subscriptions (scheduled orders) are created with fixed, regularly bought items and can be configured for buying at regular intervals. A customer creates a recurring order with an online grocery store to have the same groceries delivered every Tuesday at 6:00 PM
When planning for replenishment orders, the business team need to consider the following type of situations,
- What are the options for order schedules (Days / Weeks / Months)
- Order is placed in the backend process. How do fulfilment teams handle out of stock situations?
- Do businesses allow customers to change the order schedule after creation
- Can customers ask to cancel or reschedule a particular instance of order?
Please note that order fulfilment and billing process for replenishment product orders are smilur to regular order management and billing process.
Please refer Replenishment Order for more details.
Volume-Based Subscription products have both an initial price as well as on-going prices. For products with subscriptions, prices are often relative to the subscription's duration, The reference solution offered with SBG offers following periods of time:
- Monthly
- Quarterly
- Semi-annually
- Annually
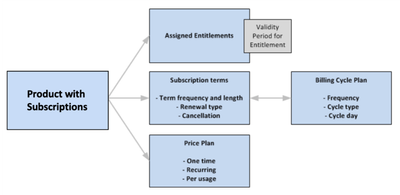
Subscription Terms: They specify what are terms of a subscription and length of a customer's commitment. Subscription terms are related to Billing Cycle Plan .
Price Plan: It defines what are the periodic charges depending on length of the commitment.
Please refer the following link for Configuring Subscription in SAP Commerce cloud, Subscription Model
SAP Subscription Billing Integration Module
SAP Commerce Cloud integration with SAP Subscription Billing using SAP Business Technology Platform helps to monetize your subscription and usage-based services, sell them across channels and touch points, bill them, collect and recognize revenue. The following are the main features of the subscription billing
Subscription Management: The integration of SAP Commerce Cloud with SAP Subscription Billing enables you to sell subscription products and provides customers with the convenience of managing their subscriptions right from the storefront.
Customer Replication: A B2C customer registered in the SAP Commerce Cloud is replicated to SAP Subscription Billing using SAP Cloud Integration.
Subscription Product Replication: A digital subscription product created in SAP Subscription Billing is replicated to SAP Commerce Cloud using SAP Cloud Integration.
Order Replication: Sales order placed in the SAP Commerce Cloud storefront is replicated to SAP Subscription Billing and SAP S/4HANA based on the type of product.
Unified Order Processing: This generic and unified order process enables sending subscription orders to SAP Subscription Billing, based on the external consignment fulfilment framework.
Please refer the following for detailed information, architecture, and implementation of the subscription integration
- SAP Subscription Billing Integration Module
- SAP Entitlement Management Integration Module
- SAP Commerce Cloud Integration with SAP Subscription Billing
Conclusion
This article was developed to address some key difference between two type of subscriptions and help the business / IT team to plan and strategize their implementation. This may help to perform a gap analysis, evaluating dependencies and available options for the implementation. For more information, please refer to the resources referred to in each section of this article. Thank you for your time .
- SAP Managed Tags:
- SAP Commerce,
- SAP Commerce Cloud,
- SAP Subscription Billing
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
Business Trends
270 -
Business Trends
13 -
chitchat
1 -
customerexperience
1 -
Event Information
256 -
Event Information
18 -
Expert Insights
30 -
Expert Insights
51 -
Life at SAP
133 -
Life at SAP
1 -
Product Updates
666 -
Product Updates
28 -
SAP HANA Service
1 -
SAPHANACloud
1 -
SAPHANAService
1 -
Technology Updates
453 -
Technology Updates
15
- The Power of Nurturing: Increasing Conversion Rates and Customer Engagement in CRM and CX Blogs by SAP
- SAP Commerce Cloud Q3 ’23 Release Highlights in CRM and CX Blogs by SAP
- SAP Commerce Cloud Q2 ’23 Release Highlights in CRM and CX Blogs by SAP
- 3 steps to protect your sender reputation and your email eco system in CRM and CX Blogs by SAP
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 10 | |
| 8 | |
| 4 | |
| 2 | |
| 1 | |
| 1 | |
| 1 | |
| 1 | |
| 1 | |
| 1 |