- SAP Community
- Groups
- Interest Groups
- Enterprise Architecture
- Blog Posts
- SAP Reference Architecture Content: An Overview – ...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Disclaimer:
- Information provided in this blog serves only as a general overview and does not replace any legal agreements between SAP and its contractual parties. As this blog may not be updated regularly, please refer to your assigned SAP Account or Partner Manager for up-to-date information, especially regarding roadmaps, licensing, and pricing models.
- The SAP Reference Solution Architecture (at solution value flow level) provides a first orientation and high-level implementation guidance while covering a broad business and solution scope. Based on the breadth of the scope covered as well as the high-level nature (e.g. the guidance assumes a complete adoption of the SAP portfolio which is rarely the case in a real customer situation), SAP recommends assessing the architecture guidance in the context of a specific customer scenario. Additional integration development and enhancements might be required to achieve the desired outcome.
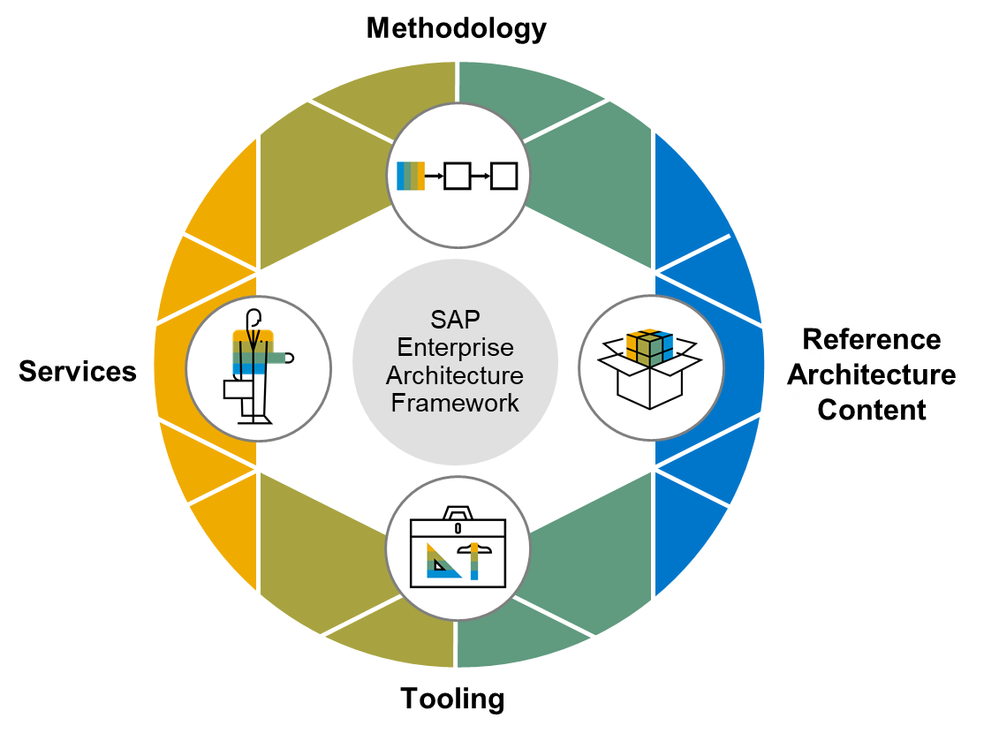
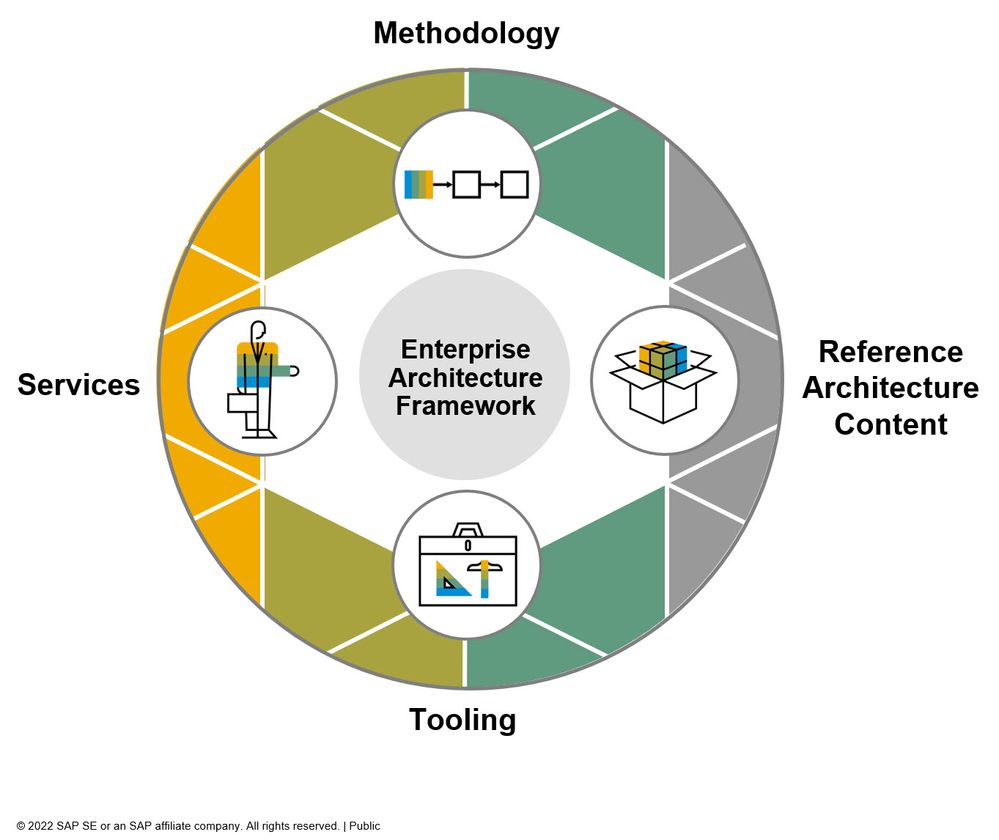
The blog SAP Reference Architecture Content: An Overview [1] explained how the standardized SAP Reference Architecture Content follows the SAP Enterprise Architecture Methodology, which aims to align Business Architecture Domain with IT Solution Architecture Domain.
Figure 1 - SAP Enterprise Architecture Methodology – Linking Business and IT
Based on the SAP Enterprise Architecture Methodology, the standardized SAP Reference Architecture content provides a harmonized Business and Solution Architecture reference content which supports the Business and IT alignment by mapping business capabilities and processes with IT solutions. As such, it is composed of 2 parts:
- SAP Reference Business Architecture (RBA) describes the scope and undertaking of any enterprise, in a business-centric and product-agnostic way.
- SAP Reference Solution Architecture (RSA) explores how SAP addresses a customer’s business challenge with its unique product portfolio.
In this blog, we will take a closer look at the SAP Reference Solution Architecture Content (RSA) – what it is, how it is structured, and how it complements the SAP Reference Business Architecture (RBA).
A closer look at the SAP Reference Solution Architecture (RSA)
The SAP Reference Solution Architecture (RSA) shows how certain SAP products interact to realize a business process. It presents an implementable solution architecture, which is composed of different elements and has been created based on guidance from the SAP Product Engineering unit.
Capability Perspective – Bridging business and IT at the strategic-level
In the SAP Reference Business Architecture (RBA), the Business Capability describes the “what”, specifically the ability an enterprise needs to deliver value to its customers.
Equivalent to the Business Capability, the SAP Reference Solution Architecture (RSA) introduces the concept of the Solution Capability.
The Solution Capability describes the “how”, particularly how a Business Capability can be concretely implemented by one or more Solution Components. Multiple Solution Capabilities can exist for a Business Capability when there are different ways to implement the Business Capability. The SAP Reference Solution Architecture provides a high-level recommendation on the most suitable Solution Capability for a specific business context.
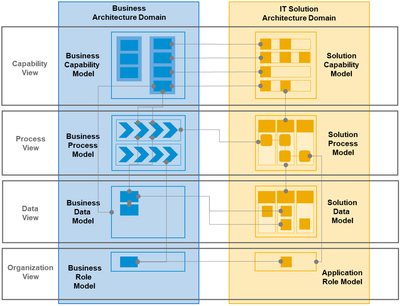
Below is a simplified illustration of the relationship between Business Capability, Solution Capability and Solution Component.
Figure 2 – Example of Solution Capability
The Solution Capability associates the Solution Component needed to realize a Business Capability. A Solution Component represents a single or a group of software products. There can be one or multiple mandatory Solution Components that are needed to realize the minimum viable scope of the Business Capability. In addition, there can be optional Solution Components that provide enhanced features, for example with respect to automation or optimization. If there are multiple Solution Components involved, they are typically technically integrated.
Process Perspective – Bridging business and IT at the operational-level
In the SAP Reference Business Architecture (RBA), an enterprise is described using 8 end-to-end Business Process patterns. An end-to-end Business Process contains Business Activities, which describe how value is generated by using certain Business Capabilities.
Corresponding to the Business Process, the SAP Reference Solution Architecture (RSA) has the concept of the Solution Process, Solution Value Flow, and Solution Process Flow.
The Solution Process is an implementation of a Business Process, using a defined set of Solution Components. A Solution Component represents a single or a group of software products.
In the SAP Reference Solution Architecture, there are various architectural artefacts that represent the Solution Process. One such architectural artefact is the Solution Value Flow, which displays the activities supported by the set of Solution Components.
Below is a simplified illustration of a Solution Value Flow, which shows only a partial content for the Process Module “Deliver Service to Fulfill”.
Figure 3 – Example of Solution Value Flow
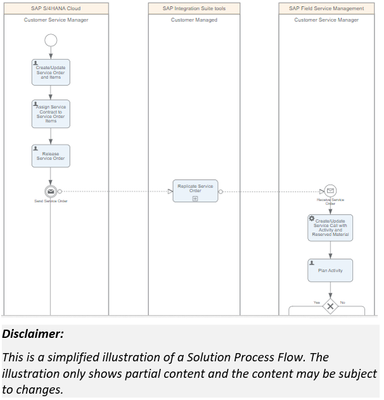
On the other hand, the Solution Process Flows are more detailed diagrams, which depict the control flow and the specific sequence of steps in the process flow. The Solution Process Flow uses the Business Process Model Notation (BPMN).
Below is a simplified illustration of a Solution Process Flow, which shows only a partial content for the Service Order process flow.
Figure 4 – Example of Solution Process Flow
In Summary
The SAP Reference Architecture Content helps align Business and IT by mapping business challenges with IT solutions. It is composed of two parts:
- SAP Reference Business Architecture (RBA) describes the scope and undertaking of any enterprise, in a business-centric and product-agnostic way.
- SAP Reference Solution Architecture (RSA) explores how SAP addresses a customer’s business challenge with its unique product portfolio.
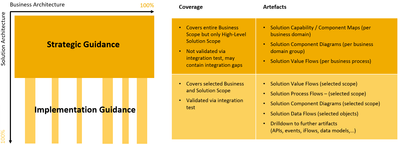
The long-term vision of the SAP Reference Architecture Content is to support customers in their business transformation, from discovering the recommended SAP solutions, understanding their business impact, and supporting their technical implementation along an integrated business process. Thus, the SAP Reference Solution Architecture contains different architectural artefacts. For strategic guidance, artefacts such as Solution Value Flows and Solution Capability Model cover a broad scope, focusing on the end-to-end Business Process. On the other hand, artefacts such as APIs, events, and data model provide technical implementation guidance, but only for a limited business and solution scope.
Figure 5 – SAP Reference Solution Architecture - From Strategy to Implementation
Do you want access to the SAP Reference Architecture Content? The SAP Reference Architecture Content is available as part of the One Process Acceleration Layer practice. SAP Signavio Process Explorer [2], the gateway to access and explore content generated as part of the One Process Acceleration Layer practice, will be generally available in January 2023.
Reference
[1] SAP Reference Architecture Content: An Overview
[2] SAP Signavio Process Explorer
- SAP Managed Tags:
- SAP Signavio,
- SAP Signavio Process Manager
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
Application Architecture
23 -
Business Architecture
33 -
Data Architecture
19 -
Emerging Trends
20 -
Enterprise Architecture
55 -
Frameworks
21 -
Hybrid and Multi Cloud
3 -
Innovation
14 -
Integration Architecture
17 -
Portuguese
1 -
Roadmaps
12 -
Skills and Learning
29 -
Solution Architecture
22 -
Sustainability
3 -
Technology Architecture
23 -
Tools
14
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 3 | |
| 1 | |
| 1 | |
| 1 | |
| 1 |